13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(9):3849-3866. doi:10.7150/thno.39706 This issue Cite
Review
Aptamer-guided extracellular vesicle theranostics in oncology
1. School of Medicine and Centre for Molecular and Medical Research, Deakin University, Waurn Ponds, Victoria, Australia
2. Division of Genetics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital/Harvard Medical School, 77 Avenue Louise Pasteur, Boston, MA 02115, USA
3. Department for Management of Science and Technology Development, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
4. Faculty of Pharmacy, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
5. Translational Medical Center, The Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital, 28 Fuxing Road, Haidian District, Beijing, China, 100853
6. Institute for Frontier Materials, Deakin University, Waurn Ponds, Victoria, 3216, Australia
7. School of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences, Monash University, 27 Rainforest Walk, Clayton VIC 3800, Australia
8. Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhengzhou University, He'nan Key Laboratory of Tumor Pathology, Zhengzhou 450052, China
9. Cancer Care Centre, St George Hospital, Kogarah, and St George and Sutherland Clinical School, University of New South Wales, Kensington, NSW, Australia
10. Laboratory of Tumor Molecular and Cellular Biology, College of Life Sciences, Shaanxi Normal University, 620 West Chang'an Avenue, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710119, China
11. CAS Key Laboratory of Nano-Bio Interface, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215123, China
12. Clinical School, Luohe Medical College, 148, Daxue Road, Luohe City, Henan Province, 462000, China
13. Department of General Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, 1055 Sanxiang Road, Suzhou, P.R. China, 215004
14. GenePharma-Deakin Joint Laboratory of Aptamer Medicine, Suzhou 215123, China and Waurn Ponds, Victoria 3216, Australia
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
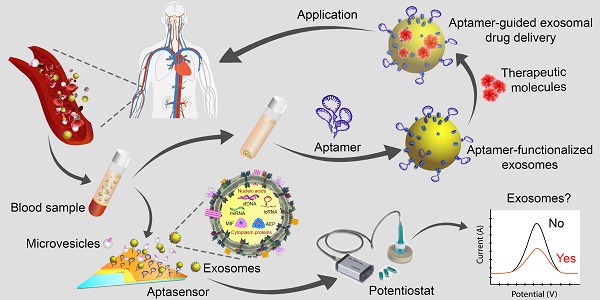
In the past decade, the study of exosomes, nanosized vesicles (50-150 nm) released into the extracellular space via the fusion of multivesicular bodies with the plasma membrane, has burgeoned with impressive achievements in theranostics applications. These nanosized vesicles have emerged as key players in homeostasis and in the pathogenesis of diseases owing to the variety of the cargos they can carry, the nature of the molecules packaged inside the vesicles, and the robust interactions between exosomes and target cells or tissues. Accordingly, the development of exosome-based liquid biopsy techniques for early disease detection and for monitoring disease progression marks a new era of precision medicine in the 21st century. Moreover, exosomes possess intrinsic properties - a nanosized structure and unique "homing effects" - that make them outstanding drug delivery vehicles. In addition, targeted exosome-based drug delivery systems can be further optimized using active targeting ligands such as nucleic acid aptamers. Indeed, the aptamers themselves can function as therapeutic and/or diagnostic tools based on their attributes of unique target-binding and non-immunogenicity. This review aims to provide readers with a current picture of the research on exosomes and aptamers and their applications in cancer theranostics, highlighting recent advances in their transition from the bench to the clinic.
Keywords: exosomes, aptamers, theranostics, liquid biopsy, targeting
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact