13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(10):4544-4556. doi:10.7150/thno.40532 This issue Cite
Review
Tumor circulome in the liquid biopsies for cancer diagnosis and prognosis
1. Cancer Institute (Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Intervention, China National Ministry of Education), The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China
2. Institute of Translational Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310029, China
3. Department of Obstetrics, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China
4. Department of Biochemistry, College of Biomedical Sciences, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China
5. Department of Neurosurgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
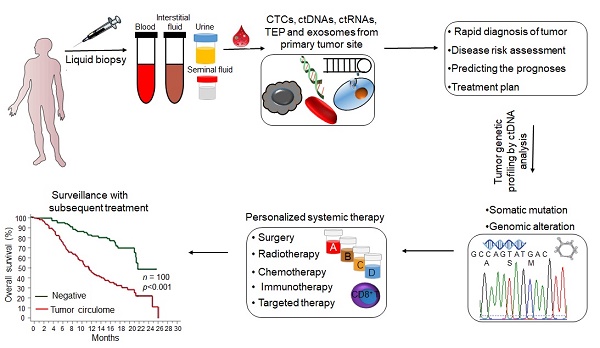
Liquid biopsy is a convenient, fast, non-invasive and reproducible sampling method that can dynamically reflect the changes in tumor gene expression profile, and provide a robust basis for individualized therapy and early diagnosis of cancer. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are the currently approved diagnostic biomarkers for screening cancer patients. In addition, tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (tdEVs), circulating tumor-derived proteins, circulating tumor RNA (ctRNA) and tumor-bearing platelets (TEPs) are other components of liquid biopsies with diagnostic potential. In this review, we have discussed the clinical applications of these biomarkers, and the factors that limit their implementation in routine clinical practice. In addition, the most recent developments in the isolation and analysis of circulating tumor biomarkers have been summarized, and the potential of non-blood liquid biopsies in tumor diagnostics has also been discussed.
Keywords: liquid biopsy, tumor circulome, tumor screening
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact