13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(10):4627-4643. doi:10.7150/thno.42869 This issue Cite
Research Paper
SLFN11 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and metastasis by targeting RPS4X via mTOR pathway
1. Department of Liver Surgery, Liver Cancer Institute, Zhongshan Hospital, and Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Cancer Invasion (Ministry of Education), Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
2. Department of Molecular and Cellular Oncology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA.
3. Biomedical Research Centre, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
4. Institute of Fudan Minhang Academic Health System, and Key Laboratory of Whole-period Monitoring and Precise Intervention of Digestive Cancer (SMHC), Minhang Hospital & AHS, Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
5. Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
6. Graduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences and Center for Molecular Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
*The authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
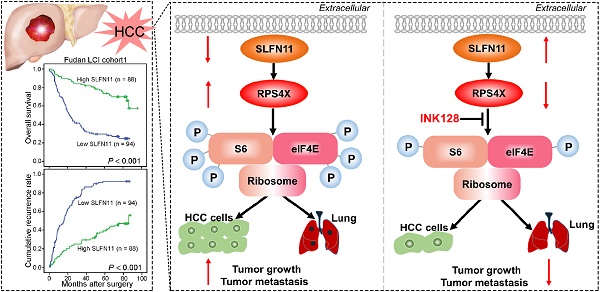
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains one of the most refractory malignancies worldwide. Schlafen family member 11 (SLFN11) has been reported to play an important role in inhibiting the production of human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1). However, whether SLFN11 also inhibits hepatitis B virus (HBV), and affects HBV-induced HCC remain to be systematically investigated.
Methods: qRT-PCR, western blot and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining were conducted to investigate the potential role and prognostic value of SLFN11 in HCC. Then SLFN11 was stably overexpressed or knocked down in HCC cell lines. To further explore the potential biological function of SLFN11 in HCC, cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assays, colony formation assays, wound healing assays and transwell cell migration and invasion assays were performed in vitro. Meanwhile, HCC subcutaneous xenograft tumor models were established for in vivo assays. Subsequently, immunoprecipitation (IP) and liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analyses were applied to understand the molecular mechanisms of SLFN11 in HCC. Co-IP, immunofluorescence and IHC staining were used to analyze the relationship between ribosomal protein S4 X-linked (RPS4X) and SLFN11. Finally, the therapeutic potential of SLFN11 with mTOR pathway inhibitor INK128 on inhibiting HCC growth and metastasis was evaluated in vitro and in vivo orthotopic xenograft mouse models.
Results: We demonstrate that SLFN11 expression is decreased in HCC, which is associated with shorter overall survival and higher recurrence rates in patients. In addition, we show that low SLFN11 expression is associated with aggressive clinicopathologic characteristics. Moreover, overexpression of SLFN11 inhibits HCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, facilitates apoptosis in vitro, and impedes HCC growth and metastasis in vivo, all of which are attenuated by SLFN11 knockdown. Mechanistically, SLFN11 physically associates with RPS4X and blocks the mTOR signaling pathway. In orthotopic mouse models, overexpression of SLFN11 or inhibition of mTOR pathway inhibitor by INK128 reverses HCC progression and metastasis.
Conclusions: SLFN11 may serve as a powerful prognostic biomarker and putative tumor suppressor by suppressing the mTOR signaling pathway via RPS4X in HCC. Our study may therefore offer a novel therapeutic strategy for treating HCC patients with the mTOR pathway inhibitor INK128.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, Schlafen family member 11, mTOR inhibitor, ribosomal protein S4 X-linked, prognostic biomarker
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact