13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(12):5305-5321. doi:10.7150/thno.42445 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Bio-orthogonal click-targeting nanocomposites for chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy in breast cancer
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines and Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Drug Stability of Biopharmaceuticals, Department of Pharmaceutics, China Pharmaceutical University, 24 Tongjiaxiang, Nanjing 210009, China.
*Authors contributed equally.
Abstract
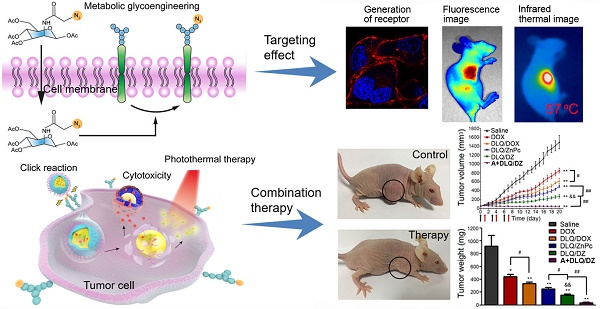
Chemo-photothermal synergistic treatment has a high potential to complement traditional cancer therapy and amplify its outcome. Precision in the delivery of these therapeutic agents to tumor cells has been indicated as being key to maximizing their therapeutic effects.
Method: We developed a bio-orthogonal copper-free click-targeting nanocomposite system (DLQ/DZ) that markedly improved specific co-delivery of the chemotherapeutic agent doxorubicin and the photosensitizer zinc phthalocyanine to breast cancer cells via a two-step mechanism. In the first step, an azide-modified sugar (tetraacetylated N-azidoacetyl-D-mannosamine, Ac4ManNAz) was injected intratumorally for glycoengineering of the tumor cell surface. Subsequently, DLQ/DZ was administered to achieve tumor enrichment via bio-orthogonal copper-free click-targeting.
Results: During the first step in our experiments, high density azide groups (3.23×107/cell) were successfully glycoengineered on the surface of tumor cells following Ac4ManNAz administration in vitro. Subsequently, the highly efficient bio-orthogonal click chemical reaction between receptor-like azide groups on tumor cells and DBCO on nanocomposites significantly enhanced the cellular uptake and tumor-specific distribution (4.6x increase) of the nanocomposites in vivo. Importantly, Ac4ManNAz+DLQ/DZ treatment augmented the anti-cancer effect of combined chemotherapy and PTT (96.1% inhibition rate), nearly ablating the tumor.
Conclusions: This bio-orthogonal click-targeting combination strategy may provide a promising treatment approach for surficial breast cancers.
Keywords: nanocomposite, chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy, metabolic glycoengineering, bio-orthogonal click chemistry, breast cancer
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact