13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(12):5368-5383. doi:10.7150/thno.41171 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Heritable modifiers of the tumor microenvironment influence nanoparticle uptake, distribution and response to photothermal therapy
1. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA
2. Department of Radiology, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA
3. Simmons Cancer Institute, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, IL, USA
4. Department of Medical Microbiology, Immunology, and Cell Biology, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, IL, USA
5. Department of Radiation Oncology, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA
6. Department of Physiology, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA
7. Genomic Sciences and Precision Medicine Center, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI 53226, USA
*Both authors have contributed equally
Abstract
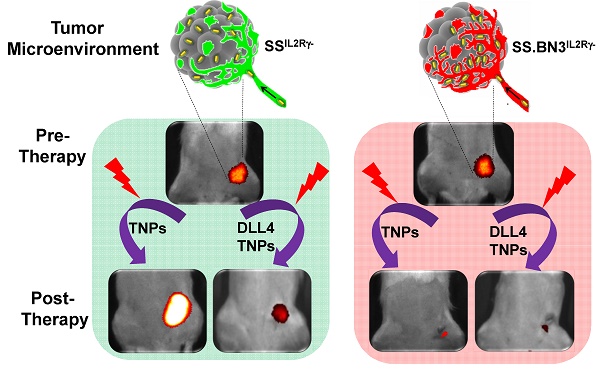
We report the impact of notch-DLL4-based hereditary vascular heterogeneities on the enhanced permeation and retention (EPR) effect and plasmonic photothermal therapy response in tumors.
Methods: We generated two consomic rat strains with differing DLL4 expression on 3rd chromosome. These strains were based on immunocompromised Salt-sensitive or SSIL2Rγ- (DLL4-high) and SS.BN3IL2Rγ- (DLL4-low) rats with 3rd chromosome substituted from Brown Norway rat. We further constructed three novel SS.BN3IL2Rγ- congenic strains by introgressing varying segments of BN chromosome 3 into the parental SSIL2Rγ- strain to localize the role of SSIL2Rγ- DLL4 on tumor EPR effect with precision. We synthesized multimodal theranostic nanoparticles (TNPs) based on Au-nanorods which provide magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-ray, and optical contrasts to assess image guided PTT response and quantify host specific therapy response differences in tumors orthotopically xenografted in DLL4-high and -low strains. We tested recovery of therapy sensitivity of PTT resistant strains by employing anti-DLL4 conjugated TNPs in two triple negative breast cancer tumor xenografts.
Results: Host strains with high DLL4 allele demonstrated slightly increased tumor nanoparticle uptake but consistently developed photothermal therapy resistance compared to tumors in host strains with low DLL4 allele. Tumor micro-environment with low DLL4 expression altered the geographic distribution of nanoparticles towards closer proximity with vasculature which improved efficacy of PTT in spite of lower overall TNP uptake. Targeting TNPs to tumor endothelium via anti-DLL4 antibody conjugation improved therapy sensitivity in high DLL4 allele hosts for two triple negative human breast cancer xenografts.
Conclusions: Inherited DLL4 expression modulates EPR effects in tumors, and molecular targeting of endothelial DLL4 via nanoparticles is an effective personalized nanomedicine strategy.
Keywords: Nanoparticles, Photothermal, Tumor Microenvironment, Breast Cancer, Tumor Vasculature
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact