13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(12):5398-5411. doi:10.7150/thno.41725 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Integrative metagenomic and metabolomic analyses reveal severity-specific signatures of gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease
1. Department of Nephrology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Keelung, Taiwan
2. College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan
3. Institute of Statistics, National Tsing-Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
4. Kidney Research Center, Department of Nephrology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkuo, Taiwan
5. Department of Health Policy and Management, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, US
6. Department of Mathematical Sciences, Florida Atlantic University, Florida, US
7. Biotools, Co., Ltd, New Taipei City, Taiwan
8. Department of Computer Science, Florida Atlantic University, Florida, US
9. Whole-Genome Research Core Laboratory of Human Diseases, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Keelung, Taiwan
10. Department of Medical Biotechnology and Laboratory Science, and Microbiota Research Center, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan
11. Central Research Laboratory, XiaMen Chang Gung Hospital, XiaMen, China
12. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial hospital, Linkuo, Taiwan
Abstract
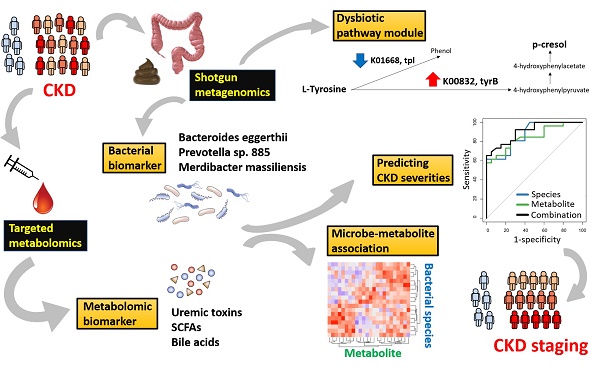
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a serious healthcare dilemma, associated with specific changes in gut microbiota and circulating metabolome. Yet, the functional capacity of CKD microbiome and its intricate relationship with the host metabolism at different stages of disease are less understood. Methods: Here, shotgun sequencing of fecal samples and targeted metabolomics profiling of serum bile acids, short- and medium-chain fatty acids, and uremic solutes were performed in a cohort of CKD patients with different severities and non-CKD controls. Results: We identified that levels of 13 microbial species and 6 circulating metabolites were significantly altered across early to advanced stages or only in particular stage(s). Among these, Prevotella sp. 885 (decreased) was associated with urea excretion, while caproic acid (decreased) and p-cresyl sulfate (elevated) were positively and negatively correlated with the glomerular filtration rate, respectively. In addition, we identified gut microbial species linked to changes in circulating metabolites. Microbial genes related to secondary bile acid biosynthesis were differentially abundant at the early stage, while pathway modules related to lipid metabolism and lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis were enriched in the CKD microbiome at the advanced stage, suggesting that changes in microbial metabolism and host inflammation may contribute to renal health. Further, we identified metagenomic and metabolomic markers to discriminate cases of different severities from the controls, among which Bacteroides eggerthii individually was of particular value in early diagnosis. Conclusions: Our dual-omics data reveal the connections between intestinal microbes and circulating metabolites perturbed in CKD, which may be of etiological and diagnostic importance.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease, Gut microbiome, Serum metabolites, Short-chain fatty acid, Uremic solute
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact