13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(13):5687-5703. doi:10.7150/thno.42087 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A S100A14-CCL2/CXCL5 signaling axis drives breast cancer metastasis
1. The State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, China
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, China
3. Medical College, Guizhou University, Guizhou, 550025, China
4. Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, China
# These authors contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
Rationale: Chemokines contribute to cancer metastasis and have long been regarded as attractive therapeutic targets for cancer. However, controversy exists about whether neutralizing chemokines by antibodies promotes or inhibits tumor metastasis, suggesting that the approach to directly target chemokines needs to be scrutinized.
Methods: Transwell assay, mouse metastasis experiments and survival analysis were performed to determine the functional role of S100A14 in breast cancer. RNA-Seq, secreted proteomics, ChIP, Western blot, ELISA, transwell assay and neutralizing antibody experiments were employed to investigate the underlying mechanism of S100A14 in breast cancer metastasis. Immunohistochemistry and ELISA were performed to examine the expression and serum levels of S100A14, CCL2 and CXCL5, respectively.
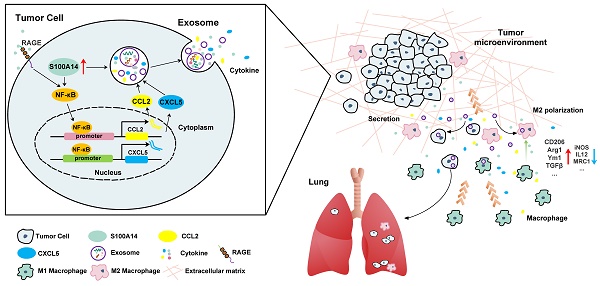
Results: Overexpression of S100A14 significantly enhanced migration, invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells. In contrast, knockout of S100A14 exhibited the opposite effects. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that S100A14 promotes breast cancer metastasis by upregulating the expression and secretion of CCL2 and CXCL5 via NF-κB mediated transcription. The clinical sample analyses showed that S100A14 expression is strongly associated with CCL2/CXCL5 expression and high expression of these three proteins is correlated with worse clinical outcomes. Notably, the serum levels of S100A14, CCL2/CXCL5 have significant diagnostic value for discerning breast cancer patients from healthy individuals.
Conclusions: S100A14 is significantly upregulated in breast cancer, it can promote breast cancer metastasis by increasing the expression and secretion of CCL2/CXCL5 via RAGE-NF-κB pathway. And S100A14 has the potential to serve as a serological marker for diagnosis of breast cancer. Collectively, we identify S100A14 as an upstream regulator of CCL2/CXCL5 signaling and a metastatic driver of breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer, Metastasis, S100A14, CCL2, CXCL5
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact