13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(13):5879-5894. doi:10.7150/thno.43894 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Interleukin-22 drives a metabolic adaptive reprogramming to maintain mitochondrial fitness and treat liver injury
1. Minhang Hospital & Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Immunotherapeutics, School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
2. Department of Ophthalmology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto CA 94304, USA
3. Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Virology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanghai Medical College of Fudan University
4. Department of Nephrology, Changhai Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, China
5. Department of Pharmacy, Huadong Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
6. Tongcheng Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Anhui 231400, P. R. China
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
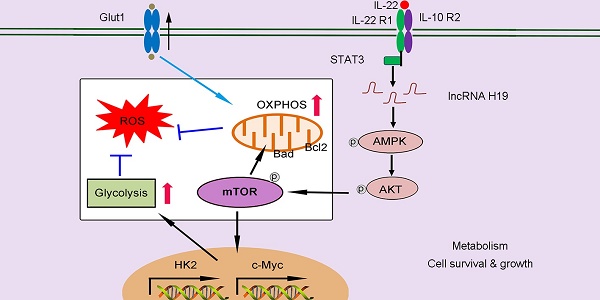
Rationale: Interleukin 22 (IL-22) is an epithelial survival cytokine that is at present being explored as therapeutic agents for acute and chronic liver injury. However, its molecular basis of protective activities remains poorly understood.
Methods: Here we demonstrate that IL-22 inhibits the deteriorating metabolic states induced by stimuli in hepatocytes. Utilizing cell biological, molecular, and biochemical approaches, we provide evidence that IL-22 promotes oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and glycolysis and regulates the metabolic reprogramming related transcriptional responses.
Results: IL-22 controls metabolic regulators and enzymes activity through the induction of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), AKT and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), thereby ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction. The upstream effector lncRNA H19 also participates in the controlling of these metabolic processes in hepatocytes. Importantly, amelioration of liver injury by IL-22 through activation of metabolism relevant signaling and regulation of mitochondrial function are further demonstrated in cisplatin-induced liver injury and steatohepatitis.
Conclusions: Collectively, our results reveal a novel mechanism underscoring the regulation of metabolic profiles of hepatocytes by IL-22 during liver injury, which might provide useful insights from the bench to the clinic in treating and preventing liver diseases.
Keywords: oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis, mitochondria, reactive oxygen species, lncRNA H19
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact