13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(16):7131-7149. doi:10.7150/thno.44564 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Bacterial extracellular vesicle-coated multi-antigenic nanovaccines protect against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection by modulating antigen processing and presentation pathways
1. College of Veterinary Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China.
2. Institute of Comparative Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China.
3. Jiangsu Co-innovation Center for Prevention and Control of Important Animal Infectious Diseases and Zoonoses, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China.
4. Joint International Research Laboratory of Agriculture and Agri-Product Safety, the Ministry of Education of China, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China.
Abstract
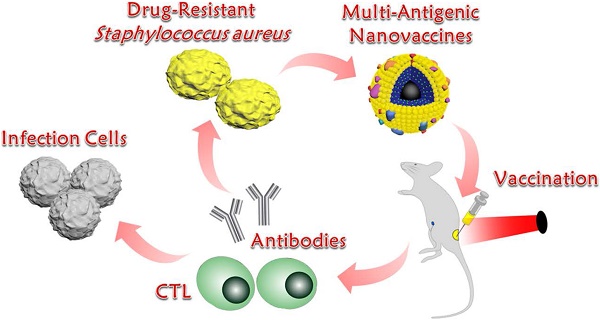
Background: Vaccination provides an alternative to antibiotics in addressing drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infection. However, vaccine potency is often limited by a lack of antigenic breadth and a demand on the generation of antibody responses alone.
Methods: In this study, bacterial extracellular vesicles (EVs) coating indocyanine green (ICG)-loaded magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) were constructed as multi-antigenic vaccines (EV/ICG/MSN) with the ability to modulate antigen presentation pathways in dendritic cells (DCs) to induce cellular immune responses.
Results: Exposing the EV/ICG/MSNs to a laser could promote DC maturation and enhance the proteasome-dependent antigen presentation pathway by facilitating endolysosomal escape, improving proteasome activity, and elevating MHC-I expression. Immunization by EV/ICG/MSNs with laser irradiation in vivo triggered improved CD8+ T cell responses while maintaining CD4+ T cell responses and humoral immunity. In addition, in vivo tracking data revealed that the vaccine could be efficiently transported from the injection site into lymph nodes. Skin infection experiments showed that the vaccine not only prevented and treated superficial infection but also decreased bacterial invasiveness, thus strongly suggesting that EV/ICG/MSNs were effective in preventing complications resulting from the introduction of S. aureus infections.
Conclusion: This multi-antigenic nanovaccine-based modulation of antigen presentation pathways provides an effective strategy against drug-resistant S. aureus infection.
Keywords: bacterial extracellular vesicles, nanovaccines, drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, cross-presentation, CD8+ T cells
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact