13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(18):8315-8342. doi:10.7150/thno.45922 This issue Cite
Review
Mitochondrial Sirtuin 3: New emerging biological function and therapeutic target
1. State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center and Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Biotherapy, Chengdu 610041, China.
2. Anti-Stress and Health Research Center, College of Pharmacy, Jinan University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510632, China.
Abstract
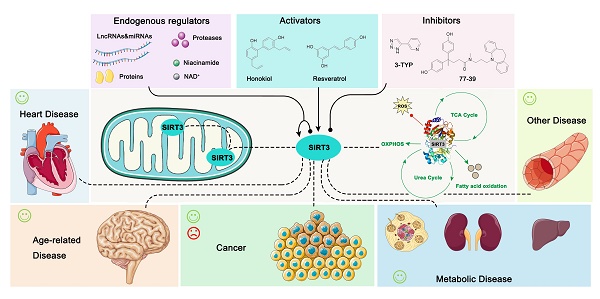
Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) is one of the most prominent deacetylases that can regulate acetylation levels in mitochondria, which are essential for eukaryotic life and inextricably linked to the metabolism of multiple organs. Hitherto, SIRT3 has been substantiated to be involved in almost all aspects of mitochondrial metabolism and homeostasis, protecting mitochondria from a variety of damage. Accumulating evidence has recently documented that SIRT3 is associated with many types of human diseases, including age-related diseases, cancer, heart disease and metabolic diseases, indicating that SIRT3 can be a potential therapeutic target. Here we focus on summarizing the intricate mechanisms of SIRT3 in human diseases, and recent notable advances in the field of small-molecule activators or inhibitors targeting SIRT3 as well as their potential therapeutic applications for future drug discovery.
Keywords: SIRT3, Mitochondrial homeostasis, Age-related disease, Cancer, SIRT3 activator, SIRT3 inhibitor
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact