13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(20):9364-9377. doi:10.7150/thno.48107 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Efficacy and safety of 225Ac-PSMA-617 targeted alpha therapy in metastatic castration-resistant Prostate Cancer patients
1. Department of Nuclear Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India.
2. Department of Medical Oncology, BR Ambedkar Rotary Cancer Hospital, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India.
3. Department of Urology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India.
*These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
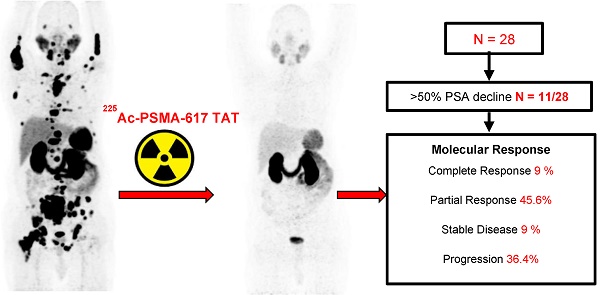
Rationale: Despite the success of several standards of care treatment options in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), a significant number of patients attain therapeutic resistance and eventually develop disease progression. Managing these patients are currently challenging. Hence, there is an unmet need for further efficient therapeutic options that induce anti-tumor activity and improve survival. The objective of this study was to assess the safety and therapeutic efficacy of 225Ac-PSMA-617 targeted alpha therapy (TAT) in mCRPC patients in real-world conditions.
Methods: In this prospective study, we recruited patients with mCRPC who either were refractory to 177Lu-PSMA-617 radioligand therapy (RLT) or did not receive previous 177Lu-PSMA-617 RLT. Patients were treated with 225Ac-PSMA-617 TAT (100 KBq/Kg body weight) at 8-weekly intervals. The primary endpoint included the assessment of biochemical response by measuring the serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response rate as per the prostate cancer working group criteria (PCWG3). Secondary endpoints comprised the estimation of overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), molecular tumor response assessment (PERCIST 1 criteria), disease control rate (DCR), toxicity according to CTCAE v5.0, and clinical response evaluation.
Results: A total of 28 patients were recruited for this cohort study among whom 15 (54%) received prior 177Lu-PSMA-617 RLT and the remaining 13 (46%) patients were 177Lu-PSMA-617 RLT naïve. The mean age was 69.7 years (range: 46-87 years). All patients, except one, had extensive skeletal metastases on baseline 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT scan; one patient had lymph node dominant disease and advanced primary prostatic tumor. The mean activity administered was 26.5 ± 12 MBq (range: 9.25 - 62.9 MBq) [715.5 ± 327 µCi, range: 250 - 1700 µCi] with a median of 3 cycles (range: 1 - 7 cycles). At 8th week of post first cycle of 225Ac-PSMA-617 therapy (initial follow-up) and the end of the follow-up, >50% decline in PSA was observed in 25% and 39%, respectively. The median PFS and OS were 12 months (95% CI: 9 - 13 months) and 17 months (95% CI: 16 months - upper limit not reached), respectively. Molecular tumor response by PERCIST 1 criteria could be conducted in 22/28 (78.6%) patients, which revealed complete response in 2/22 (9%), partial response in 10/22 (45.4%) patients, 2/22 (9%) with stable disease, and 8/22 (36%) with progressive diseases. The disease control rate, according to the biochemical and molecular tumor response criteria, was 82% and 63.6%, respectively. Multivariate analysis revealed PSA progression as adverse prognostic indicator of OS, and any PSA decline as a good prognostic indicator of PFS. There was no Grade III/IV toxicity noted in this series. The most common side-effect was transient fatigue (50%) followed by grade I/II xerostomia (29%).
Conclusion: 225Ac-PSMA-617 TAT showed promising disease control rate, even when all other therapeutic options were exhausted, with low treatment-related toxicities.
Keywords: 225Ac-PSMA-617 therapy, Targeted alpha therapy, mCRPC, efficacy, safety, salvage treatment
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact