13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(21):9721-9740. doi:10.7150/thno.44342 This issue Cite
Research Paper
HI-511 overcomes melanoma drug resistance via targeting AURKB and BRAF V600E
1. The Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, 801 16th Ave NE, Austin, MN 55912, USA.
2. Program in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455, USA.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
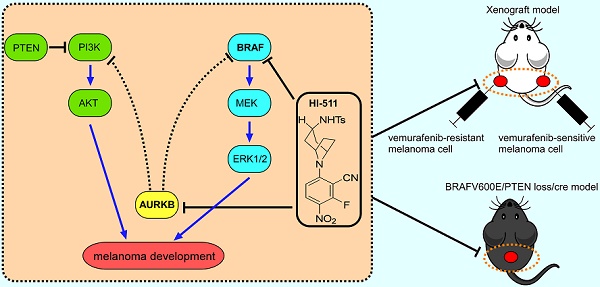
Rationale: Melanoma is an aggressive tumor of the skin and drug resistance is still a major problem in melanoma therapy. Novel targets and effective agents to overcome drug resistant melanoma are urgently needed in clinical therapy.
Methods: Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database analysis, pathway enrichment analysis, and survival rate analysis were utilized to identify a candidate target. An anchorage-independent cell growth assay, flow cytometry, Western blot, and a xenograft mouse model were used to study the function of Aurora kinase B (AURKB) in both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant melanoma. Next, HI-511, a novel dual-target inhibitor targeting both AURKB and BRAF V600E, was designed and examined by an in vitro kinase assay. Methods as indicated above in addition to a BRAF V600E/PTEN-loss melanoma mouse model were used to demonstrate the effect of HI-511 on melanoma development in vitro and in vivo.
Results: AURKB is highly expressed in melanoma and especially in vemurafenib-resistant melanoma and the expression was correlated with patient survival rate. Knocking down AURKB inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis in melanoma, which was associated with the BRAF/MEK/ERKs and PI3-K/AKT signaling pathways. Importantly, we found that HI-511, a novel dual-target inhibitor against AURKB and BRAF V600E, suppresses both vemurafenib-sensitive and vemurafenib-resistant melanoma growth in vitro and in vivo by inducing apoptosis and mediating the inhibition of the BRAF/MEK/ERKs and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways.
Conclusion: AURKB is a potential target for melanoma treatment. HI-511, a novel dual-target inhibitor against both AURKB and BRAF V600E, could achieve durable suppression of melanoma growth, even drug-resistant melanoma growth.
Keywords: HI-511, AURKB, BRAF V600E, vemurafenib-resistant melanoma, melanoma
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact