13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(1):330-345. doi:10.7150/thno.51004 This issue Cite
Research Paper
TDP-43 proteinopathy impairs mRNP granule mediated postsynaptic translation and mRNA metabolism
1. Department of Medicine, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan.
2. Institute of Clinical Medicine, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan.
3. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, UC Davis Medical Center, California, USA.
4. Research Center of Clinical Medicine, National Cheng Kung University Hospital, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan.
Abstract
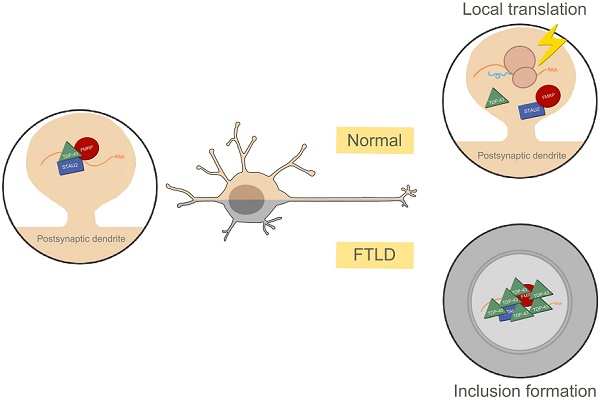
Background: Local protein synthesis and mRNA metabolism mediated by mRNP granules in the dendrites and the postsynaptic compartment is essential for synaptic remodeling and plasticity in neuronal cells. Dysregulation of these processes caused by TDP-43 proteinopathy leads to neurodegenerative diseases, such as frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Methods: Using biochemical analysis and imaging techniques, including super-resolution microscopy, we provide evidence, for the first time, for the postsynaptic localization of TDP-43 in mammalian synapses and we show that TDP-43 is a component of neuronal mRNP granules.
Results: With activity stimulation and various molecular approaches, we further demonstrate activity-dependent mRNP granule dynamics involving disassembly of mRNP granules, release of mRNAs, activation of local protein translation, and the impairment of granule disassembly in cellular, animal and human models of TDP-43 proteinopathy.
Conclusion: Our study elucidates the interplay between TDP-43 and neuronal mRNP granules in normal physiology and TDP-43 proteinopathy in the regulation of local protein translation and mRNA metabolism in the postsynaptic compartment.
Keywords: TDP-43, mRNP granule, postsynaptic, local translation, super-resolution microscopy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact