13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(2):805-823. doi:10.7150/thno.50230 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hexosamine biosynthetic pathway promotes the antiviral activity of SAMHD1 by enhancing O-GlcNAc transferase-mediated protein O-GlcNAcylation
1. Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Infectious Diseases (Ministry of Education), Institute for Viral Hepatitis, Department of Infectious Diseases, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Proteomics, Beijing Proteome Research Center, National Center for Protein Sciences (Beijing), Beijing Institute of Lifeomics, Beijing, China.
3. School of Pharmaceutical Science, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China.
4. The First Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
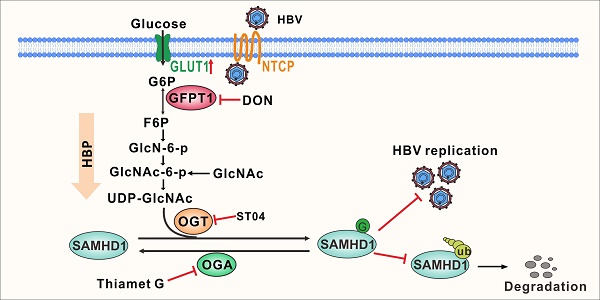
Rationale: Viruses hijack the host cell machinery to promote viral replication; however, the mechanism by which metabolic reprogramming regulates innate antiviral immunity in the host remains elusive. Herein, we explore how the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway (HBP) and O-linked-N-acetylglucosaminylation (O-GlcNAcylation) regulate host antiviral response against hepatitis B virus (HBV) in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: We conducted a metabolomics assay to evaluate metabolic responses of host cells to HBV infection. We systematically explored the role of HBP and protein O-GlcNAcylation in regulating HBV infection in cell and mouse models. O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) target proteins were identified via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and co-immunoprecipitation assays. Additionally, we also examined uridine diphosphate (UDP)-GlcNAc biosynthesis and O-GlcNAcylation levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB).
Results: HBV infection upregulated GLUT1 expression on the hepatocyte surface and facilitated glucose uptake, which provides substrates to HBP to synthesize UDP-GlcNAc, leading to an increase in protein O-GlcNAcylation. Pharmacological or transcriptional inhibition of HBP and O-GlcNAcylation promoted HBV replication. Mechanistically, O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT)-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of sterile alpha motif and histidine/aspartic acid domain-containing protein 1 (SAMHD1) on Ser93 stabilizes SAMHD1 and enhances its antiviral activity. Analysis of clinical samples revealed that UDP-GlcNAc level was increased, and SAMHD1 was O-GlcNAcylated in patients with CHB.
Conclusions: HBP-mediated O-GlcNAcylation positively regulates host antiviral response against HBV in vitro and in vivo. The findings reveal a link between HBP, O-GlcNAc modification, and innate antiviral immunity by targeting SAMHD1.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus, O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine modification, sterile alpha motif and histidine/aspartic acid domain-containing protein 1, antiviral immunity, hexosamine biosynthetic pathway
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact