13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(20):10074-10090. doi:10.7150/thno.61646 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Sult2b1 deficiency exacerbates ischemic stroke by promoting pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization in mice
1. Department of Neurosurgery, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, USA.
2. Institute of Medical Innovation and Research, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China.
3. Medical Research Center, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China.
4. The College of Forestry, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China.
5. Department of Plant Biology, Carnegie Institution for Science, Stanford, USA.
6. Shanghai Institute of Immunology, Translational Medicine Center, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
7. Research Center of Translational Medicine, Shanghai Children's hospital, State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
8. Fuwai Hospital, National Centre for Cardiovascular Diseases, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China.
9. Division of Vascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, Stanford University School of Medicine, 1201Welch Road, MSLS Building, Stanford, USA.
Abstract
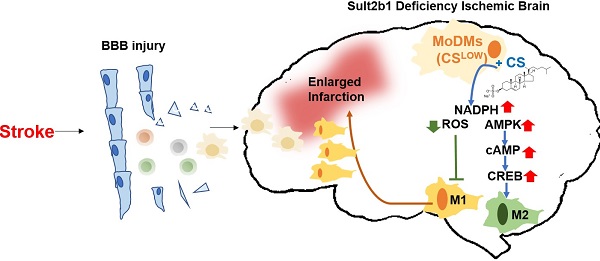
Rationale: Stroke is a leading causes of human death worldwide. Ischemic damage induces the sterile neuroinflammation, which directly determines the recovery of patients. Lipids, a major component of the brain, significantly altered after stroke. Cholesterol sulfate, a naturally occurring analog of cholesterol, can directly regulate immune cell activation, indicating the possible involvement of cholesterol metabolites in neuroinflammation. Sulfotransferase family 2b member 1 (Sult2b1) is the key enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of cholesterol sulfate. This study aimed to investigate the function of Sult2b1 and cholesterol sulfate in the neuroinflammation after ischemic stroke.
Methods and Results: Sult2b1-/- and wild-type mice were subjected to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Our data showed that Sult2b1-/- mice had larger infarction and worse neurological scores. To determine whether immune cells were involved in the worsening stroke outcome in Sult2b1-/- mice, bone marrow transplantation, immune cell depletion, and adoptive monocyte transfer were performed. Combined with CyTOF and immunofluorescence techniques, we demonstrated that after stroke, the peripheral monocyte-derived macrophages were the dominant cell type promoting the pro-inflammatory status in Sult2b1-/-mice. Using primary bone marrow-derived macrophages, we showed that cholesterol sulfate could attenuate the pro-inflammatory polarization of macrophages under both normal and oxygen-glucose deprivation conditions by regulating the levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and activating the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) - cAMP responsive element-binding protein (CREB) signaling pathway.
Conclusions: Sult2b1-/- promoted the polarization of macrophages into pro-inflammatory status. This trend could be attenuated by adding cholesterol sulfate, which promotes the polarization of macrophages into anti-inflammatory status by metabolic regulation. In this study, we established an inflammation-metabolism axis during the macrophage polarization after ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Ischemic Stroke, Sult2b1, Cholesterol Sulfate, Macrophage, Neuroinflammation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact