13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(3):1162-1175. doi:10.7150/thno.53073 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Three-dimensional Imaging Coupled with Topological Quantification Uncovers Retinal Vascular Plexuses Undergoing Obliteration
1. Department of Bioengineering, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA.
2. Division of Neonatology and Developmental Biology, Department of Pediatrics, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA.
3. Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA.
4. Department of Ophthalmology, Stein Eye Institute, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA.
5. Greater Los Angeles VA Healthcare System, Los Angeles, CA.
6. Medical Engineering, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
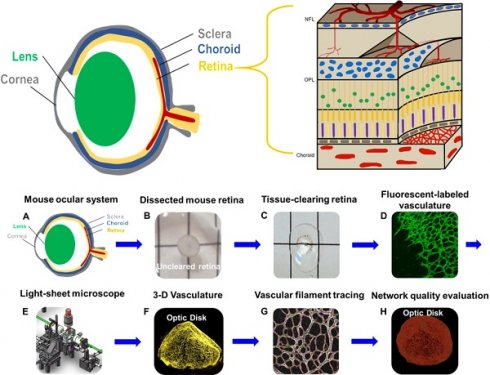
Introduction: Murine models provide microvascular insights into the 3-D network disarray seen in retinopathy and cardiovascular diseases. Light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) has emerged to capture retinal vasculature in 3-D, allowing for assessment of the progression of retinopathy and the potential to screen new therapeutic targets in mice. We hereby coupled LSFM, also known as selective plane illumination microscopy, with topological quantification, to characterize the retinal vascular plexuses undergoing preferential obliteration.
Method and Result: In postnatal mice, we revealed the 3-D retinal microvascular network in which the vertical sprouts bridge the primary (inner) and secondary (outer) plexuses, whereas, in an oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) mouse model, we demonstrated preferential obliteration of the secondary plexus and bridging vessels with a relatively unscathed primary plexus. Using clustering coefficients and Euler numbers, we computed the local versus global vascular connectivity. While local connectivity was preserved (p > 0.05, n = 5 vs. normoxia), the global vascular connectivity in hyperoxia-exposed retinas was significantly reduced (p < 0.05, n = 5 vs. normoxia). Applying principal component analysis (PCA) for auto-segmentation of the vertical sprouts, we corroborated the obliteration of the vertical sprouts bridging the secondary plexuses, as evidenced by impaired vascular branching and connectivity, and reduction in vessel volumes and lengths (p < 0.05, n = 5 vs. normoxia).
Conclusion: Coupling 3-D LSFM with topological quantification uncovered the retinal vasculature undergoing hyperoxia-induced obliteration from the secondary (outer) plexus to the vertical sprouts. The use of clustering coefficients, Euler's number, and PCA provided new network insights into OIR-associated vascular obliteration, with translational significance for investigating therapeutic interventions to prevent visual impairment.
Keywords: Light-sheet fluorescence microscopy, Primary and secondary plexus, Vertical sprouts, Oxygen-induced retinopathy, Retinal vasculature
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact