13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(4):1703-1720. doi:10.7150/thno.43895 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Proteomic analysis reveals ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting ROS production from mitochondrial complex I
1. State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu, China.
2. Clinical Metabolomics Center, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 211198, Jiangsu, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
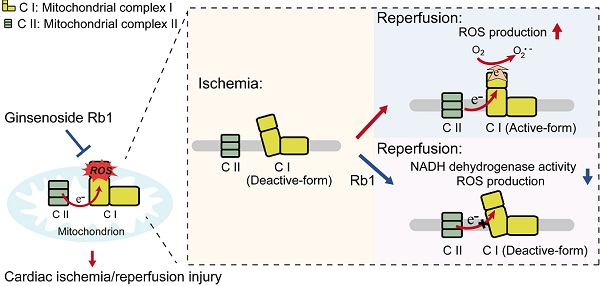
Rationale: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) burst from mitochondrial complex I is considered the critical cause of ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Ginsenoside Rb1 has been reported to protect the heart against I/R injury; however, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. This work aimed to investigate if ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates cardiac I/R injury by inhibiting ROS production from mitochondrial complex I.
Methods: In in vivo experiments, mice were given ginsenoside Rb1 and then subjected to I/R injury. Mitochondrial ROS levels in the heart were determined using the mitochondrial-targeted probe MitoB. Mitochondrial proteins were used for TMT-based quantitative proteomic analysis. In in vitro experiments, adult mouse cardiomyocytes were pretreated with ginsenoside Rb1 and then subjected to hypoxia and reoxygenation insult. Mitochondrial ROS, NADH dehydrogenase activity, and conformational changes of mitochondrial complex I were analyzed.
Results: Ginsenoside Rb1 decreased mitochondrial ROS production, reduced myocardial infarct size, preserved cardiac function, and limited cardiac fibrosis. Proteomic analysis showed that subunits of NADH dehydrogenase in mitochondrial complex I might be the effector proteins regulated by ginsenoside Rb1. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibited complex I- but not complex II- or IV-dependent O2 consumption and enzyme activity. The inhibitory effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on mitochondrial I-dependent respiration and reperfusion-induced ROS production were rescued by bypassing complex I using yeast NADH dehydrogenase. Molecular docking and surface plasmon resonance experiments indicated that ginsenoside Rb1 reduced NADH dehydrogenase activity, probably via binding to the ND3 subunit to trap mitochondrial complex I in a deactive form upon reperfusion.
Conclusion: Inhibition of mitochondrial complex I-mediated ROS burst elucidated the probable underlying mechanism of ginsenoside Rb1 in alleviating cardiac I/R injury.
Keywords: Ginsenoside Rb1, Mitochondrial complex I, Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, Proteomic analysis, Reactive oxygen species
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact