13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(5):2201-2217. doi:10.7150/thno.52717 This issue Cite
Research Paper
m6A regulator-based methylation modification patterns characterized by distinct tumor microenvironment immune profiles in colon cancer
1. Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong, 250021, China
2. Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250021, China
3. Key Laboratory of Engineering of Shandong Province, Shandong Provincial Hospital, Jinan, Shandong, 250021, China
4. Department of Gastroenterology, Key Laboratory of Engineering of Shandong Province, Shandong Provincial Hospital, Jinan, Shandong, 250021, China
5. Tianjin Sino-US Diagnostics Co., Ltd, Tianjin, China
6. Department of Radiation Oncology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research center for Cancer; Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy; Tianjin's Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin, China
7. Department of Tumor Cell Biology, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin's Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Tianjin, China
8. Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, Center for Advanced Biomedical Imaging and Photonics, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard University, Boston, 02215, MA, USA
9. Clinical Research Center of Shandong University, Clinical Epidemiology Unit, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250021, China
Abstract
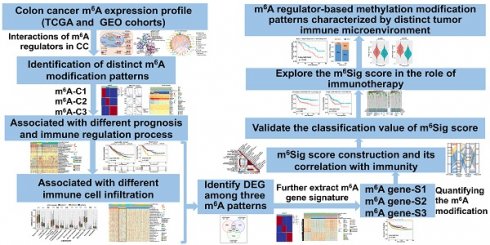
Recent studies have highlighted the biological significance of RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in tumorigenicity and progression. However, it remains unclear whether m6A modifications also have potential roles in immune regulation and tumor microenvironment (TME) formation.
Methods: In this study, we curated 23 m6A regulators and performed consensus molecular subtyping with NMF algorithm to determine m6A modification patterns and the m6A-related gene signature in colon cancer (CC). The ssGSEA and CIBERSORT algorithms were employed to quantify the relative infiltration levels of various immune cell subsets. An PCA algorithm based m6Sig scoring scheme was used to evaluate the m6A modification patterns of individual tumors with an immune response.
Results: Three distinct m6A modification patterns were identified among 1307 CC samples, which were also associated with different clinical outcomes and biological pathways. The TME characterization revealed that the identified m6A patterns were highly consistent with three known immune profiles: immune-inflamed, immune-excluded, and immune-desert, respectively. Based on the m6Sig score, which was extracted from the m6A-related signature genes, CC patients can be divided into high and low score subgroups. Patients with lower m6Sig score was characterized by prolonged survival time and enhanced immune infiltration. Further analysis indicated that lower m6Sig score also correlated with greater tumor mutation loads, PD-L1 expression, and higher mutation rates in SMGs (e.g., PIK3CA and SMAD4). In addition, patients with lower m6Sig scores showed a better immune responses and durable clinical benefits in three independent immunotherapy cohorts.
Conclusions: This study highlights that m6A modification is significantly associated with TME diversity and complexity. Quantitatively evaluating the m6A modification patterns of individual tumors will strengthen our understanding of TME characteristics and promote more effective immunotherapy strategies.
Keywords: Colon cancer, m6A modification, Tumor microenvironment, Immune profiles, Immunotherapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact