13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(5):2381-2394. doi:10.7150/thno.47627 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Multi-omics study of silicosis reveals the potential therapeutic targets PGD2 and TXA2
1. State Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Department of Pathophysiology, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Department of Physiology, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
3. Wuxi Lung Transplantation Center, Wuxi People's Hospital Affiliated with Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214023, China
4. Department of Thoracic Surgery and Lung Transplantation, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
5. Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
* These authors contributed equally to this article
Abstract
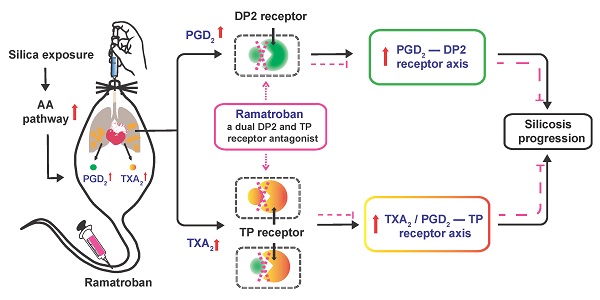
Rationale: Silicosis is a severe occupational lung disease. Current treatments for silicosis have highly limited availability (i.e., lung transplantation) or, do not effectively prolong patient survival time (i.e., lung lavage). There is thus an urgent clinical need for effective drugs to retard the progression of silicosis.
Methods: To systematically characterize the molecular changes associated with silicosis and to discover potential therapeutic targets, we conducted a transcriptomics analysis of human lung tissues acquired during transplantation, which was integrated with transcriptomics and metabolomics analyses of silicosis mouse lungs. The results from the multi-omics analyses were then verified by qPCR, western blot, and immunohistochemistry. The effect of Ramatroban on the progression of silicosis was evaluated in a silica-induced mouse model.
Results: Wide metabolic alterations were found in lungs from both human patients and mice with silicosis. Targeted metabolite quantification and validation of expression of their synthases revealed that arachidonic acid (AA) pathway metabolites, prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) and thromboxane A2 (TXA2), were significantly up-regulated in silicosis lungs. We further examined the effect of Ramatroban, a clinical antagonist of both PGD2 and TXA2 receptors, on treating silicosis using a mouse model. The results showed that Ramatroban significantly alleviated silica-induced pulmonary inflammation, fibrosis, and cardiopulmonary dysfunction compared with the control group.
Conclusion: Our results revealed the importance of AA metabolic reprogramming, especially PGD2 and TXA2 in the progression of silicosis. By blocking the receptors of these two prostanoids, Ramatroban may be a novel potential therapeutic drug to inhibit the progression of silicosis.
Keywords: silicosis, multi-omics, PGD2, TXA2, Ramatroban
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact