13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(6):2490-2504. doi:10.7150/thno.47130 This issue Cite
Research Paper
In vivo detection of teriflunomide-derived fluorine signal during neuroinflammation using fluorine MR spectroscopy
1. Berlin Ultrahigh Field Facility (B.U.F.F.), Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine, Berlin, Germany.
2. Experimental and Clinical Research Center, a joint cooperation between the Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association, Berlin, Germany.
3. Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB), Berlin, Germany.
4. MRI TOOLS GmbH, Berlin, Germany.
5. Lipidomix GmbH, Berlin, Germany.
6. Medicinal Chemistry, Leibniz-Institut fϋr Molekulare Pharmakologie (FMP), Berlin, Germany.
7. Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health (BIH), Berlin, Germany.
Abstract
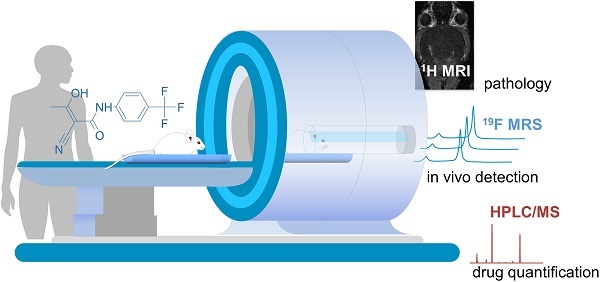
Background: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is indispensable for diagnosing neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS). MRI also supports decisions regarding the choice of disease-modifying drugs (DMDs). Determining in vivo tissue concentrations of DMDs has the potential to become an essential clinical tool for therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM). The aim here was to examine the feasibility of fluorine-19 (19F) MR methods to detect the fluorinated DMD teriflunomide (TF) during normal and pathological conditions.
Methods: We used 19F MR spectroscopy to detect TF in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mouse model of multiple sclerosis (MS) in vivo. Prior to the in vivo investigations we characterized the MR properties of TF in vitro. We studied the impact of pH and protein binding as well as MR contrast agents.
Results: We could detect TF in vivo and could follow the 19F MR signal over different time points of disease. We quantified TF concentrations in different tissues using HPLC/MS and showed a significant correlation between ex vivo TF levels in serum and the ex vivo 19F MR signal.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the feasibility of 19F MR methods to detect TF during neuroinflammation in vivo. It also highlights the need for further technological developments in this field. The ultimate goal is to add 19F MR protocols to conventional 1H MRI protocols in clinical practice to guide therapy decisions.
Keywords: MRI, MRS, Fluorine, Teriflunomide, Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, Multiple Sclerosis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact