13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(6):2770-2787. doi:10.7150/thno.51756 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Neutrophil-derived trail is a proinflammatory subtype of neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles
1. Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, 41944, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, 41944, Republic of Korea.
3. Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, 41944, Republic of Korea.
4. Department of Molecular Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, 41944, Republic of Korea.
5. Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, 24252, Republic of Korea.
6. Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, 41944, Republic of Korea.
7. Stem Cell Neuroplasticity Research Group, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, 41944, Republic of Korea.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
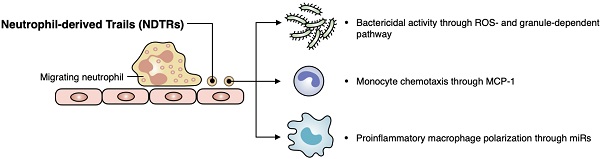
Aims: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-derived vesicles that mediate intercellular communications. Neutrophils produce different subtypes of EVs during inflammatory responses. Neutrophil-derived trails (NDTRs) are generated by neutrophils migrating toward inflammatory foci, whereas neutrophil-derived microvesicles (NDMVs) are thought to be generated by neutrophils that have arrived at the inflammatory foci. However, the physical and functional characteristics of neutrophil-derived EVs are incompletely understood. In this study, we aimed to investigate the differences between NDTRs and NDMVs.
Methods: The generation of neutrophil-derived EVs were visualized by live-cell fluorescence images and the physical characteristics were further analyzed using nanotracking analysis assay, scanning electron microscopic analysis, and marker expressions. Functional characteristics of neutrophil-derived EVs were analyzed using assays for bactericidal activity, monocyte chemotaxis, phenotype polarization of macrophages, and miRNA sequencing. Finally, the effects of neutrophil-derived EVs on the acute and chronic inflammation were examined in vivo.
Results: Both EVs share similar characteristics including stimulators, surface marker expression, bactericidal activity, and chemoattractive effect on monocytes via MCP-1. However, the integrin-mediated physical interaction was required for generation of NDTRs whereas NDMV generation was dependent on PI3K pathway. Interestingly, NDTRs contained proinflammatory miRNAs such as miR-1260, miR-1285, miR-4454, and miR-7975, while NDMVs contained anti-inflammatory miRNAs such as miR-126, miR-150, and miR-451a. Although both EVs were easily uptaken by monocytes, NDTRs enhanced proinflammatory macrophage polarization whereas NDMVs induced anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization. Moreover, NDTRs showed protective effects against lethality in a murine sepsis model and pathological changes in a murine chronic colitis model.
Conclusion: These results suggest that NDTR is a proinflammatory subtype of neutrophil-derived EVs distinguished from NDMV.
Keywords: EV, extracellular vesicle, NDMV, neutrophil-derived microvesicle, NDTR, neutrophil-derived trail
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact