13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(10):4910-4928. doi:10.7150/thno.56205 This issue Cite
Review
Drug repurposing for next-generation combination therapies against multidrug-resistant bacteria
1. College of Veterinary Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, Jiangsu, China.
2. Jiangsu Co-innovation Center for Prevention and Control of Important Animal Infectious Diseases and Zoonoses, Joint International Research Laboratory of Agriculture and Agri-Product Safety, the Ministry of Education of China, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, Jiangsu, China.
3. Institute of Comparative Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, Jiangsu, China.
4. School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Plymouth, Drake Circus, Plymouth, UK.
Abstract
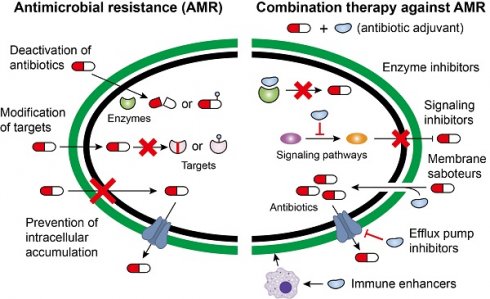
Antimicrobial resistance has been a global health challenge that threatens our ability to control and treat life-threatening bacterial infections. Despite ongoing efforts to identify new drugs or alternatives to antibiotics, no new classes of antibiotic or their alternatives have been clinically approved in the last three decades. A combination of antibiotics and non-antibiotic compounds that could inhibit bacterial resistance determinants or enhance antibiotic activity offers a sustainable and effective strategy to confront multidrug-resistant bacteria. In this review, we provide a brief overview of the co-evolution of antibiotic discovery and the development of bacterial resistance. We summarize drug-drug interactions and uncover the art of repurposing non-antibiotic drugs as potential antibiotic adjuvants, including discussing classification and mechanisms of action, as well as reporting novel screening platforms. A pathogen-by-pathogen approach is then proposed to highlight the critical value of drug repurposing and its therapeutic potential. Finally, general advantages, challenges and development trends of drug combination strategy are discussed.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance, antibiotic adjuvants, combination therapies, drug repurposing, multidrug-resistant bacteria
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact