13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(11):5174-5196. doi:10.7150/thno.56471 This issue Cite
Review
Development of nucleic acid aptamer-based lateral flow assays: A robust platform for cost-effective point-of-care diagnosis
1. Centre for Molecular Medicine and Innovative Therapeutics, Murdoch University, Perth 6150, Australia.
2. Perron Institute for Neurological and Translational Science, Perth 6009, Australia.
3. Guangdong Key Laboratory for Research and Development of Nature Drugs, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, China.
* These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
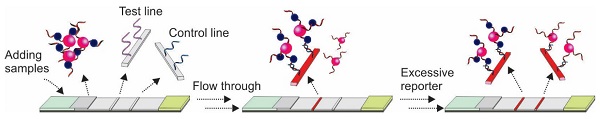
Lateral flow assay (LFA) has made a paradigm shift in the in vitro diagnosis field due to its rapid turnaround time, ease of operation and exceptional affordability. Currently used LFAs predominantly use antibodies. However, the high inter-batch variations, error margin and storage requirements of the conventional antibody-based LFAs significantly impede its applications. The recent progress in aptamer technology provides an opportunity to combine the potential of aptamer and LFA towards building a promising platform for highly efficient point-of-care device development. Over the past decades, different forms of aptamer-based LFAs have been introduced for broad applications ranging from disease diagnosis, agricultural industry to environmental sciences, especially for the detection of antibody-inaccessible small molecules such as toxins and heavy metals. But commercial aptamer-based LFAs are still not used widely compared with antibodies. In this work, by analysing the key issues of aptamer-based LFA design, including immobilization strategies, signalling methods, and target capturing approaches, we provide a comprehensive overview about aptamer-based LFA design strategies to facilitate researchers to develop optimised aptamer-based LFAs.
Keywords: Aptamer, lateral flow assay, point-of-care, biosensor, sandwich assay, competitive assay.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact