13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(12):5889-5910. doi:10.7150/thno.56157 This issue Cite
Review
High fat diet, gut microbiome and gastrointestinal cancer
1. Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Hospital, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China.
2. Shandong Engineering & Technology Research Center for Tumor Marker Detection, Jinan, Shandong, China.
3. Shandong Provincial Clinical Medicine Research Center for Clinical Laboratory, Jinan, Shandong, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
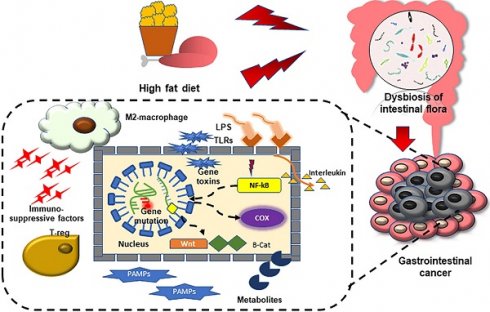
Gastrointestinal cancer is currently one of the main causes of cancer death, with a large number of cases and a wide range of lesioned sites. A high fat diet, as a public health problem, has been shown to be correlated with various digestive system diseases and tumors, and can accelerate the occurrence of cancer due to inflammation and altered metabolism. The gut microbiome has been the focus of research in recent years, and associated with cell damage or tumor immune microenvironment changes via direct or extra-intestinal effects; this may facilitate the occurrence and development of gastrointestinal tumors. Based on research showing that both a high fat diet and gut microbes can promote the occurrence of gastrointestinal tumors, and that a high fat diet imbalances intestinal microbes, we propose that a high fat diet drives gastrointestinal tumors by changing the composition of intestinal microbes.
Keywords: high fat diet, gastrointestinal cancer, gut microbiome, inflammation, metabolic reprogramming
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact