13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(13):6427-6444. doi:10.7150/thno.53229 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Neoantigen landscape in metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
1. Department of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, 651 Dongfeng East Road, Guangzhou 510060, P. R. China.
2. Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine.
3. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Diagnosis and Therapy, Guangzhou 510060, China.
4. Department of Ultrasound, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, 651 Dongfeng East Road, Guangzhou 510060, P. R. China.
5. Department of Musculoskeletal Oncology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, 651 Dongfeng East Road, Guangzhou 510060, P. R. China.
6. Department of Neurosurgery, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, 651 Dongfeng East Road, Guangzhou 510060, P. R. China.
7. Department of Breast Oncology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, 51 Dongfeng East Road, Guangzhou 510060, P. R. China.
8. Department of Minimally Invasive Interventional Radiology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, 51 Dongfeng East Road, Guangzhou 510060, P. R. China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: Reportedly, nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients with MHC I Class aberration are prone to poor survival outcomes, which indicates that the deficiency of tumor neoantigens might represent a mechanism of immune surveillance escape in NPC.
Methods: To clearly delineate the landscape of neoantigens in NPC, we performed DNA and RNA sequencing on paired primary tumor, regional lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis samples from 26 patients. Neoantigens were predicted using pVACseq pipeline. Subtype prediction model was built using random forest algorithm.
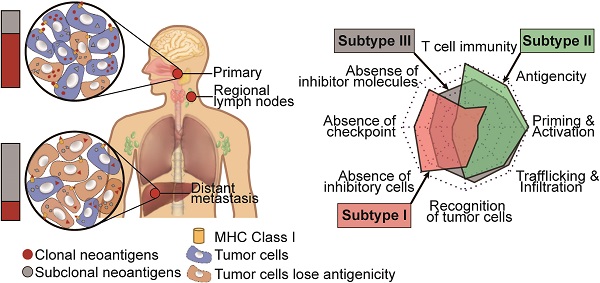
Results: Portraying the landscape of neoantigens in NPC for the first time, we found that the neoantigen load of NPC was above average compared to that of other cancers in The Cancer Genome Atlas program. While the quantity and quality of neoantigens were similar among primary tumor, regional lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis samples, neoantigen depletion was more severe in metastatic sites than in primary tumors. Upon tracking the clonality change of neoantigens, we found that neoantigen reduction occurred during metastasis. Building a subtype prediction model based on reported data, we observed that subtype I lacked T cells and suffered from severe neoantigen depletion, subtype II highly expressed immune checkpoint molecules and suffered from the least neoantigen depletion, and subtype III was heterogenous.
Conclusions: These results indicate that neoantigens are conducive to the guidance of clinical treatment, and personalized therapeutic vaccines for NPC deserve deeper basic and clinical investigations to make them feasible in the future.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, neoantigens, subtype, metastasis, microenvironment
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact