13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(17):8254-8269. doi:10.7150/thno.60160 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Promote Cx43-Overexpression of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Efficient Suicide Gene Therapy during Glioma Treatment
1. Zhejiang Province Key Laboratory of Anti-Cancer Drug Research, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China.
2. Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Key Laboratory of Clinical Cancer Pharmacology and Toxicology Research of Zhejiang Province, Affiliated Hangzhou First People's Hospital, Cancer Center, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, 310006, China.
3. Dr. Li Dak Sum & Yip Yio Chin Center for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China.
4. Department of Pharmacy, the Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310009, China.
5. State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, the First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310003, China.
6. Department of Pharmacy, Zhejiang University City College, Hangzhou 310015, China.
7. Cancer Center, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310058, China.
#These authors contributed equally: Ai Li and Tianyuan Zhang.
Abstract
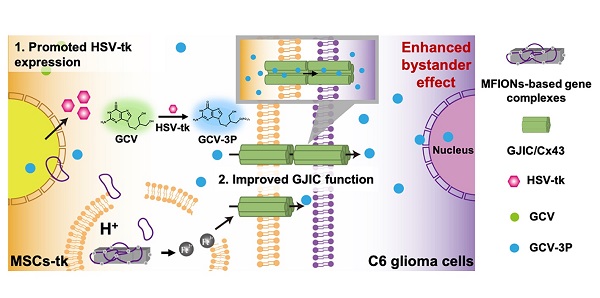
Background: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been applied as a promising vehicle for tumour-targeted delivery of suicide genes in the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSV-tk)/ganciclovir (GCV) suicide gene therapy against malignant gliomas. The efficiency of this strategy is largely dependent on the bystander effect, which relies on high suicide gene expression levels and efficient transportation of activated GCV towards glioma cells. However, up to now, the methods to enhance the bystander effect of this strategy in an efficient and safe way are still lacking and new approaches to improve this therapeutic strategy are required.
Methods: In this study, MSCs were gene transfected using magnetosome-like ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanochains (MFIONs) to highly express HSV-tk. Both the suicide and bystander effects of HSV-tk expressed MSCs (MSCs-tk) were quantitatively evaluated. Connexin 43 (Cx43) expression by MSCs and glioma cells was measured under different treatments. Intercellular communication between MSCs and C6 glioma cells was examined using a dye transfer assay. Glioma tropism and the bio-distribution of MSCs-tk were observed. Anti-tumour activity was investigated in the orthotopic glioma of rats after intravenous administration of MSCs-tk followed by intraperitoneal injection of GCV.
Results: Gene transfection using MFIONs achieved sufficient expression of HSV-tk and triggered Cx43 overexpression in MSCs. These Cx43 overexpressing MSCs promoted gap junction intercellular communication (GJIC) between MSCs and glioma cells, resulting in significantly inhibited growth of glioma through an improved bystander effect. Outstanding tumour targeting and significantly prolonged survival with decreased tumour size were observed after the treatment using MFION-transfected MSCs in glioma model rats.
Conclusion: Our results show that iron oxide nanoparticles have the potential to improve the suicide gene expression levels of transfected MSCs, while promoting the GJIC formation between MSCs and tumour cells, which enhances the sensitivity of glioma cells to HSV-tk/GCV suicide gene therapy.
Keywords: Mesenchymal stem cells, Glioma, Suicide gene, Gap junction, Iron oxide nanoparticles
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact