13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(18):9009-9021. doi:10.7150/thno.59728 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CD4+ T cell-mimicking nanoparticles encapsulating DIABLO/SMAC mimetics broadly neutralize HIV-1 and selectively kill HIV-1-infected cells
1. Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Pediatrics, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, California, USA.
2. Department of Nanoengineering, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, California, United States of America.
3. Moores Cancer Center, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, California, United States of America.
4. Rady Children's Hospital, San Diego, California, United States of America.
*Current Address: Hillhouse Capital Management, New York, New York, United States of America.
#Current Address: Prothena Corporation, South San Francisco, California, United States of America.
Abstract
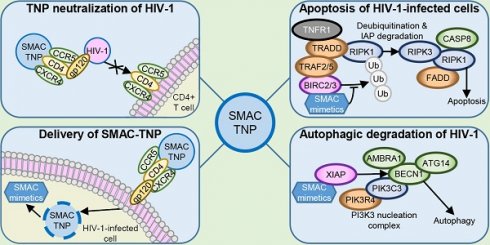
HIV-1 is a major global health challenge. The development of an effective vaccine and a therapeutic cure are top priorities. The creation of vaccines that focus an antibody response toward a particular epitope of a protein has shown promise, but the genetic diversity of HIV-1 stymies this progress. Therapeutic strategies that provide effective and broad‐spectrum neutralization against HIV-1 infection are highly desirable.
Methods: We investigated the potential of nanoengineered CD4+ T cell membrane-coated nanoparticles (TNP) encapsulating the DIABLO/SMAC mimetics LCL-161 or AT-406 (also known as SM-406 or Debio 1143) to both neutralize HIV-1 and selectively kill HIV-1-infected resting CD4+ T cells and macrophages.
Results: DIABLO/SMAC mimetic-loaded TNP displayed outstanding neutralizing breadth and potency, and selectively kill HIV-1-infected cells via autophagy-dependent apoptosis while having no drug-induced off-target or cytotoxic effects on bystander cells. Genetic inhibition of early stages of autophagy abolishes this effect.
Conclusion: DIABLO/SMAC mimetic loaded TNP have the potential to be used as therapeutic agents to neutralize cell-free HIV-1 and to kill specifically HIV-1-infected cells as part of an HIV-1 cure strategy.
Keywords: HIV, nanoparticle, SMAC mimetics, autophagy, neutralization
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact