13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(4):1937-1951. doi:10.7150/thno.53147 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Unlabeled aspirin as an activatable theranostic MRI agent for breast cancer
1. Division of MR Research, The Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science; The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD.
2. Division of Cancer Imaging Research, The Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science; The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD.
3. The Department of Biological Chemistry, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD.
4. Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD.
5. F.M. Kirby Research Center for Functional Brain Imaging, Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore, MD.
6. Department of Medical Laboratory, The Central Hospital of Wuhan, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
*KowsalyaDevi Pavuluri and Ethan Yang contributed to this study equally and share first authorship.
Abstract
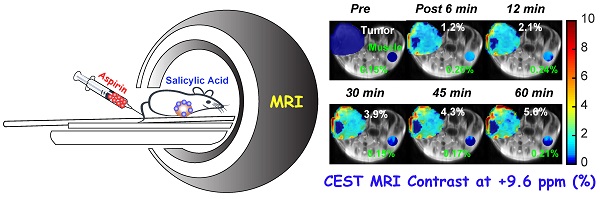
Rationale: Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is emerging as an alternative to gadolinium-based contrast MRI. We have evaluated the possibility of CEST MRI of orthotopic breast tumor xenografts with unlabeled aspirin's conversion to salicylic acid (SA) through various enzymatic activities, most notably inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1/-2 enzymes.
Methods: We measured the COX-1/-2 expression in four breast cancer cell lines by Western Blot analysis and selected the highest and lowest expressing cell lines. We then performed CEST MRI following aspirin treatment to detect SA levels and ELISA to measure levels of downstream prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). We also injected aspirin into the tail vein of mice growing orthotopic tumor xenografts which expressed high and low COX-1/-2 and acquired SA CEST MR images of these tumor xenografts for up to 70 minutes. Tumors were then harvested to perform Western Blot and ELISA experiments to measure COX-1/-2 expression and PGE2 levels, respectively.
Results: Western Blots determined that SUM159 cells contained significantly higher COX-1/-2 expression levels than MDA-MB-231 cells, in line with higher levels of downstream PGE2. SA CEST MRI yielded similar contrast at approximately 3% for both cell lines, independent of COX-1/-2 expression level. PGE2 levels decreased by about 50% following aspirin treatment. Results from our mouse study aligned with cultured cells, the overall SA CEST MRI contrast in both MDA-MB-231 and SUM159 tumor xenograft models was 5~8% at one hour post injection. PGE2 levels were ten times higher in SUM159 than MDA-MB-231 and decreased by 50%. The CEST contrast directly depended on the injected dose, with ~6%, ~3% and ~1.5% contrast observed following injection of 100 µL of 300 mM, 200 mM and 150 mM aspirin, respectively.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate the feasibility of using aspirin as a noninvasive activatable CEST MRI contrast agent for breast tumor detection.
Keywords: CEST, MRI, aspirin, salicylic acid, breast cancer, gadolinium
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact