13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(6):2707-2721. doi:10.7150/thno.68437 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CD4+FoxP3+CD73+ regulatory T cell promotes cardiac healing post-myocardial infarction
1. Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200120, China
2. Research Center for Translational Medicine, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200120, China
3. Institute of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Cardiovascular Chronic Diseases, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200120, China
4. Shanghai Heart Failure Research Center, Shanghai, 200120, China
5. Department of Cardiology, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200120, China
6. Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Shanghai Institute of Immunology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
7. Department of Child Internal Medicine, Shanghai Children's Medical Center, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 200127, China
8. Translational Medical Center for Stem Cell Therapy, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University, Shanghai 200120, China
9. Shanghai Institute of Stem Cell Research and Clinical Translation, Shanghai 200120, China
* Dr. Zhuang and Dr. Meng contributed equally to this work
Abstract
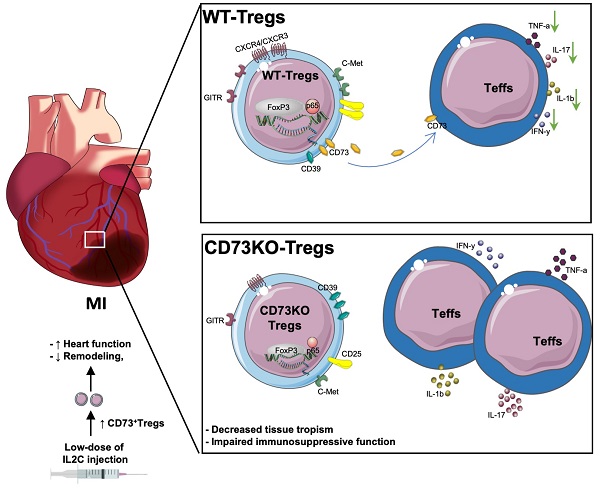
Rationale: Despite recent studies indicating a crucial role of ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) on T cells in cardiac injury after ischemia/reperfusion, the involvement of CD73+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) in cardiac repair post-myocardial infarction (MI) remains unclear. We sought to investigate the contribution of CD73 on Tregs to the resolution of cardiac inflammation and remodeling after MI.
Methods: Cardiac function, tissue injury, Tregs percentage in injured hearts, and purinergic signaling changes in cardiac FoxP3+ Tregs were analyzed after permanent descending coronary artery ligation. CD73 knockout Tregs were used to determine the function of CD73 on Tregs. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients and matched non-MI subjects were assessed via flow cytometry.
Results: Cardiac Tregs exhibited distinction of purinergic signaling post MI with dramatically high level of CD73 compared to the sham Tregs. CD73 deficiency decreased the tissue tropism, and impaired the immunosuppressive and protective function of Tregs in cardiac healing. Administration of low-dose of IL-2/anti-IL-2 complex resulted in FoxP3+CD73+Tregs expansion in the heart and contributed to the recovery of cardiac function. CD73 derived from FoxP3+Tregs could bind to FoxP3- effector T-cells and inhibit the production of multiple inflammatory cytokines. In AMI patients, CD73 expressions on both CD4+ cells and FoxP3+Tregs decreased in PBMCs. Moreover, CD73 expressions on CD4+ T cells were negatively correlated with the levels of NT pro-BNP and myocardial zymogram in serum.
Conclusions: Our findings indicated the importance of FoxP3+CD73+Tregs in inflammation resolution and cardiac healing post-MI.
Keywords: Regulatory T cells (Tregs), ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73), myocardial infarction (MI), cardiac healing, IL-2/anti-IL-2 complex
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact