13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(8):3911-3927. doi:10.7150/thno.70557 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Sequentially targeting and intervening mutual Polo-like Kinase 1 on CAFs and tumor cells by dual targeting nano-platform for cholangiocarcinoma treatment
1. Department of Gastroenterology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China.
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Drum Tower Clinical Medical College of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China.
3. Department of Pharmacy, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Drum Tower Clinical Medical College of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China.
4. Department of Bioinformatics, School of Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211166, Jiangsu Province, China.
5. Department of Pathology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China.
6. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China.
7. Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China.
8. Nanjing Medical Center for Clinical Pharmacy, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China.
*These authors have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
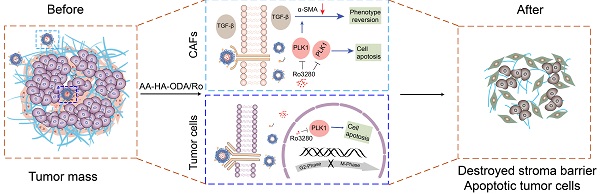
Rationale: Synergistic treatment strategies for two or more drugs have gradually developed as the main options in clinics for cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) owing to the complicated crosstalk between the tumor and stroma. However, the different synergetic mechanisms pose great challenges to the dosages and order of administration of drugs. Thus, a strategy for exploring and intervening in mutual targets derived from stromal cells and cholangiocarcinoma cells was proposed.
Methods: Genes with overexpression patterns in tumors and displaying a significant association with overall survival were identified from RNA-seq data of human CCA patients and CCA mouse models. Western blotting, qRT-PCR, immunofluorescence (IF), colony formation and flow cytometry assays were conducted to determine the biological roles of the key oncogene in cholangiocarcinoma and stromal cells respectively. Additionally, a dual-targeting drug delivery system (AA-HA-ODA) for cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and tumor cells was constructed to verify the effectiveness of intervening the screened genes in vivo.
Results: Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) was verified to play vital role in the malignant proliferation of CCA by regulating the cell cycle pathway. PLK1 also decreased stromal production by regulating the CAF phenotype. In addition, a PLK1 inhibitor (Ro3280) loaded dual-targeting drug delivery system (AA-HA-ODA) was prepared and exhibited high affinity for CAFs and cholangiocarcinoma cells. The in vivo distribution pattern and antitumor efficacy of AA-HA-ODA/Ro also verify the effectiveness of inhibiting PLK1 in CCA in vivo.
Conclusion: In summary, PLK1 is a mutual target derived from tumor cells and stroma due to its crucial role in the proliferation of tumor cells and stroma regulation in CAFs, which might provide enlightenment for multitarget treatment strategies and guidance for clinical cholangiocarcinoma treatment.
Keywords: polo-like kinase 1, cholangiocarcinoma, stroma, drug delivery system, targeting, CAFs
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact