13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(13):5986-5994. doi:10.7150/thno.75847 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Reduced splenic uptake on 68Ga-Pentixafor-PET/CT imaging in multiple myeloma - a potential imaging biomarker for disease prognosis
1. Department of Internal Medicine II, University Hospital of Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany.
2. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital of Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany.
3. Nuclear Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Augsburg, Augsburg, Germany.
4. Department of Hematology, Oncology and Cancer Immunology, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Corporate Member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany.
5. Department of Internal Medicine V, Heidelberg University Hospital, Heidelberg, Germany.
6. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Klinikum rechts der Isar, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany.
7. The Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA.
8. Technical University Munich, School of Medicine, Klinikum rechts der Isar, Clinic and Policlinic for Internal Medicine III, Munich, Germany.
9. Pharmaceutical Radiochemistry, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany.
10. Institute of Pathology, University of Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany.
#These authors equally contributed to this manuscript.
Abstract
Beyond being a key factor for tumor growth and metastasis in human cancer, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) is also highly expressed by a number of immune cells, allowing for non-invasive read-out of inflammatory activity. With two recent studies reporting on prognostic implications of the spleen signal in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in patients with plasma cell dyscrasias, the aim of this study was to correlate splenic 68Ga-Pentixafor uptake in multiple myeloma (MM) with clinical parameters and to evaluate its prognostic impact.
Methods: Eighty-seven MM patients underwent molecular imaging with 68Ga-Pentixafor-PET/CT. Splenic CXCR4 expression was semi-quantitatively assessed by peak standardized uptake values (SUVpeak) and corresponding spleen-to-bloodpool ratios (TBR) and correlated with clinical and prognostic features as well as survival parameters.
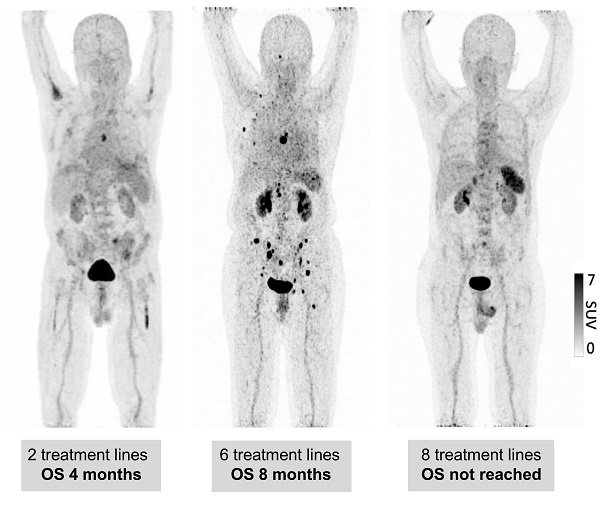
Results: 68Ga-Pentixafor-PET/CT was visually positive in all MM patients with markedly heterogeneous tracer uptake in the spleen. CXCR4 expression determined by 68Ga-Pentixafor-PET/CT corresponded with advanced disease and was inversely associated with the number of previous treatment lines as compared to controls or untreated smouldering multiple myeloma patients (SUVpeakSpleen 4.06 ± 1.43 vs. 6.02 ± 1.16 vs. 7.33 ± 1.40; P < 0.001). Moreover, reduced splenic 68Ga-Pentixafor uptake was linked to unfavorable clinical outcome. Patients with a low SUVpeakSpleen (<3.35) experienced a significantly shorter overall survival of 5 months as compared to 62 months in patients with a high SUVpeakSpleen >5.79 (P < 0.001). Multivariate Cox analysis confirmed SUVpeakSpleen as an independent predictor of survival (HR 0.75; P = 0.009).
Conclusion: These data suggest that splenic 68Ga-Pentixafor uptake might provide prognostic information in pre-treated MM patients similar to what was reported for diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Further research to elucidate the underlying biologic implications is warranted.
Keywords: multiple myeloma, 68Ga-Pentixafor-PET/CT, CXCR4, molecular imaging, spleen
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact