13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(15):6611-6625. doi:10.7150/thno.77455 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Kir6.1/K-ATP channel in astrocytes is an essential negative modulator of astrocytic pyroptosis in mouse model of depression
1. Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Neurodegeneration, Department of Pharmacology, Nanjing Medical University, 101 Longmian Avenue, Nanjing, Jiangsu 211166, P.R. China.
2. Department of Pharmacology, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, 138 Xianlin Avenue, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210023, P.R. China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
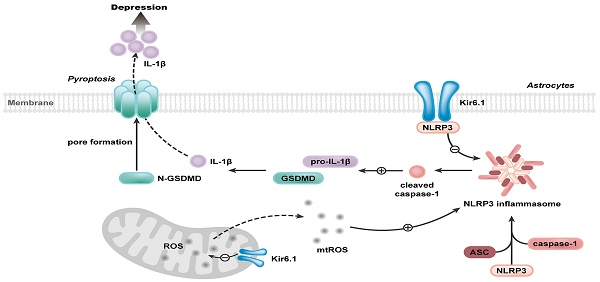
Rationale: Astrocyte dysfunction is one of the important pathological mechanisms of depression. Stress contributes to the onset of depression. As metabolic stress sensor, Kir6.1-contaning K-ATP channel (Kir6.1/K-ATP) is prominently expressed in astrocytes. However, the involvement of Kir6.1/K-ATP channel in depression remains obscure.
Methods: Astrocyte-specific Kir6.1 knockout mice were used to prepare two mouse models of depression to explore the role of astrocytic Kir6.1/K-ATP channel in depression. Primary astrocytes were cultured to reveal the underlying mechanism for Kir6.1-regulated astrocytic pyroptosis.
Results: We identified that chronic stress reduced the astrocytic Kir6.1 expression in hippocampus of mice. We further observed astrocyte-specific knockout of Kir6.1 induced depressive-like behaviors in mice. Moreover, we found that astrocytic Kir6.1 deletion increased NLRP3-mediated astrocytic pyroptosis in response to stress. Mechanistically, Kir6.1 associated with NLRP3, and this interaction prevented the assembly and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, thereby inhibition of astrocytic pyroptosis. More importantly, VX-765, an effective and selective inhibitor for NLRP3 inflammasome, could reverse the astrocytic pyroptosis and rescue the deterioration of behaviors in astrocytic Kir6.1 knockout mice.
Conclusions: Our findings illustrate that Kir6.1/K-ATP channel in astrocytes is an essential negative modulator of astrocytic pyroptosis and plays a crucial role in depression and suggest that astrocytic Kir6.1/K-ATP channel may be a promising therapeutic target for depression.
Keywords: depression, astrocyte, Kir6.1, pyroptosis, NLRP3 inflammasome
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact