13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(2):724-735. doi:10.7150/thno.79902 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dynamic white matter changes in recovered COVID-19 patients: a two-year follow-up study
1. Department of Radiology, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China
2. Department of Respiratory Medicine, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410005, China
3. MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Wuhan, China
4. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China
5. Clinical Research Center for Medical Imaging in Hunan Province, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China
6. Department of Radiology Quality Control Center, Hunan Province, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China
7. Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, the Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China
8. Hunan Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Respiratory Disease, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
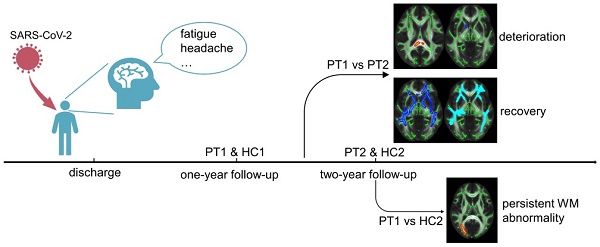
Background and purpose: Long COVID with regard to the neurological system deserves more attention, as a surge of treated patients are being discharged from the hospital. As the dynamic changes in white matter after two years remain unknown, this characteristic was the focus of this study.
Methods: We investigated 17 recovered COVID-19 patients at two years after discharge. Diffusion tensor imaging, neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging were performed to identify white matter integrity and changes from one to two years after discharge. Data for 13 revisited healthy controls were collected as a reference. Subscales of the Wechsler Intelligence scale were used to assess cognitive function. Repeated-measures ANOVA was used to detect longitudinal changes in 17 recovered COVID-19 patients and 13 healthy controls after one-year follow-up. Correlations between diffusion metrics, cognitive function, and other clinical characteristics (i.e., inflammatory factors) were also analyzed.
Results: Longitudinal analysis showed the recovery trends of large-scale brain regions, with small-scale brain region deterioration from one year to two years after SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, persistent white matter abnormalities were noted at two years after discharge. Longitudinal changes of cognitive function showed no group difference. But cross-sectional cognitive difference between recovered COVID-19 patients and revisited HCs was detected. Inflammation levels in the acute stage correlated positively with white matter abnormalities and negatively with cognitive function. Moreover, the more abnormal the white matter was at two years, the greater was the cognitive deficit present.
Conclusion: Recovered COVID-19 patients showed longitudinal recovery trends of white matter. But also had persistent white matter abnormalities at two years after discharge. Inflammation levels in the acute stage may be considered predictors of cognition and white matter integrity, and the white matter microstructure acts as a biomarker of cognitive function in recovered COVID-19 patients. These findings provide an objective basis for early clinical intervention.
Keywords: recovered COVID-19 patients, white matter changes, cognitive function, two-year follow-up, inflammation factors
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact