13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(15):5322-5347. doi:10.7150/thno.87356 This issue Cite
Review
Peptide-drug co-assembling: A potent armament against cancer
1. School of Pharmacy, Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, China.
2. Academy of Chinese Medicine Science, Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, China.
Abstract
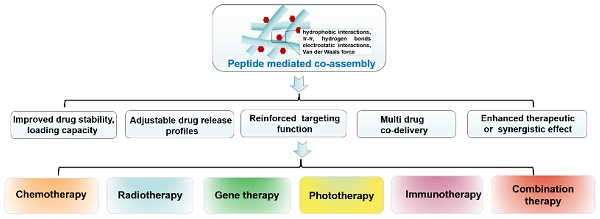
Cancer is still one of the major problems threatening human health and the therapeutical efficacies of available treatment choices are often rather low. Due to their favorable biocompatibility, simplicity of modification, and improved therapeutic efficacy, peptide-based self-assembled delivery systems have undergone significant evolution. Physical encapsulation and covalent conjugation are two common approaches to load drugs for peptide assembly-based delivery, which are always associated with drug leaks in the blood circulation system or changed pharmacological activities, respectively. To overcome these difficulties, a more elegant peptide-based assembly strategy is desired. Notably, peptide-mediated co-assembly with drug molecules provides a new method for constructing nanomaterials with improved versatility and structural stability. The co-assembly strategy can be used to design various nanostructures for cancer therapy, such as nanotubes, nanofibrils, hydrogels, and nanovesicles. Recently, these co-assembled nanostructures have gained tremendous attention for their unique superiorities in tumor therapy. This article describes the classification of assembled peptides, driving forces for co-assembly, and specifically, the design methodologies for various drug molecules in co-assembly. It also highlights recent research on peptide-mediated co-assembled delivery systems for cancer therapy. Finally, it summarizes the pros and cons of co-assembly in cancer therapy and offers some suggestions for conquering the challenges in this field.
Keywords: peptide, co-assembly, nanostructures, drug delivery, cancer therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact