13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(1):220-248. doi:10.7150/thno.87425 This issue Cite
Review
Red blood cells in biology and translational medicine: natural vehicle inspires new biomedical applications
1. Cancer Institute (Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Intervention, China National Ministry of Education), The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China, 310009.
2. Department of Biochemistry, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China, 310058.
3. Department of Biochemistry & Cancer Medicine, International Institutes of Medicine, the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Yiwu, Zhejiang, China.
4. Institute of Translational Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 310029.
5. Cancer Center, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 310029.
6. Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd.
Abstract
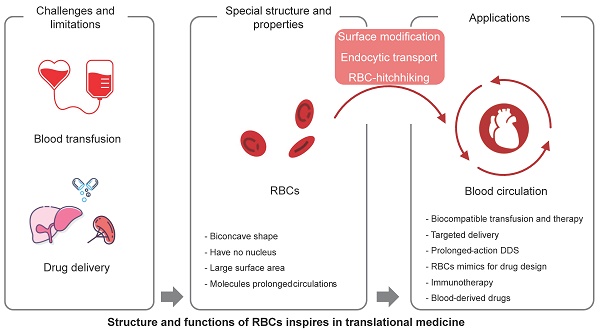
Red blood cells (RBCs) are the most abundant cell type in the blood, and play a critical role in oxygen transport. With the development of nanobiotechnology and synthetic biology, scientists have found multiple ways to take advantage of the characteristics of RBCs, such as their long circulation time, to construct universal RBCs, develop drug delivery systems, and transform cell therapies for cancer and other diseases. This article reviews the component and aging mystery of RBCs, the methods for the applied universal RBCs, and the application prospects of RBCs, such as the engineering modification of RBCs used in cytopharmaceuticals for drug delivery and immunotherapy. Finally, we summarize some perspectives on the biological features of RBCs and provide further insights into translational medicine.
Keywords: cell surface engineering, cell therapy, drug delivery, red blood cells, universal blood
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact