13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(1):392-405. doi:10.7150/thno.87243 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Imaging diagnosis and efficacy monitoring by [89Zr]Zr-DFO-KN035 immunoPET in patients with PD-L1-positive solid malignancies
1. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University; Wuxi, China.
2. Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University; Wuxi, China.
3. Dongcheng AMS Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Nanjing, China.
4. Center of Radiological Imaging, College of Medicine, Indiana University, Indiana, USA.
5. Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University; Wuxi, China.
6. Institute of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University; Wuxi, China.
7. NHC Key Laboratory of Nuclear Medicine, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Nuclear Medicine; Jiangsu Institute of Nuclear Medicine, Wuxi, China.
8. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences; Shanghai, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Rationale: Although programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitors have achieved efficacy in cancer therapy, their response rate is low. Differences in the prognosis of patients with cancer under anti-PD-L1 treatment are related to the PD-L1 level in tumors. Accurate PD-L1 detection can optimize the accuracy of tumor immunotherapy and avoid ineffective clinical diagnosis and treatments.
Methods: We investigated the imaging efficiency and therapy monitoring capacity of [89Zr]Zr-DFO-KN035 immunoPET for tumors. We labeled the monodomain anti-PD-L1 antibody KN035 with the radionuclide zirconium-89 and used this tracer for PET imaging. [89Zr]Zr-DFO-KN035 uptakes in patients with PD-L1-positive tumors, including primary and metastatic tumors, as well as in normal tissues, were comparatively assessed by using positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging.
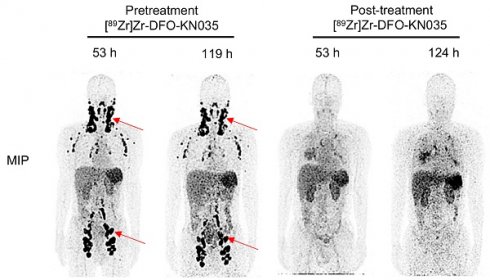
Results: In PD-L1-positive patients, [89Zr]Zr-DFO-KN035 was sensitive in tumor-targeting imaging and could detect multiple metastatic foci, including multiple bone metastases (tumor-to-muscle ratios of 7.102 and 6.118 at 55 and 120 h, respectively) and lymph-node metastases (tumor-to-muscle ratios of 11.346 and 6.542 at 55 and 120 h, respectively). The needed radioactive dose of [89Zr]Zr-DFO-KN035 (55.5-92.5 MBq) used in this study was considerably lower than that of [18F]FDG (370-555 MBq). [89Zr]Zr-DFO-KN035 monitored and predicted the site of adverse reactions in antitumor immunotherapy. Moreover, after antitumor treatment, [89Zr]Zr-DFO-KN035 enabled observational imaging for therapeutic efficacy evaluation, which can help predict patient prognosis.
Conclusion: [89Zr]Zr-DFO-KN035 can be used for the diagnosis and therapy monitoring of PD-L1-positive tumors and provide noninvasive and comprehensive observations for tumor diagnostic imaging, prognosis prediction, and efficacy evaluation.
Keywords: PD-L1 antibody, tumor immunotherapy, efficacy monitoring, molecular imaging, PET
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact