13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(3):1181-1194. doi:10.7150/thno.87916 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Discovery of novel antibacterial agent for the infected wound treatment: all-hydrocarbon stapling optimization of LL-37
1. Institute of Translational Medicine, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China.
2. School of Medicine, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China.
3. School of Pharmacy, Naval Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China.
4. Institute of Bioengineering, College of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
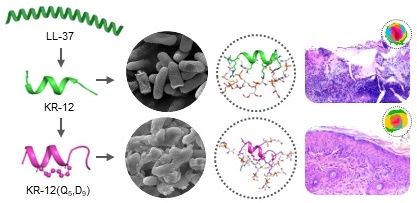
Rationale: Antimicrobial peptide LL-37 has been recognized as a favorable alternative to antibiotics due to its broad antibacterial spectrum, low resistance development and diverse biological activities. However, its high manufactory cost, poor proteolytic stability, and unpredictable cytotoxicity seriously hindered its medical translation.
Methods: To push the frontiers of its clinical application, all-hydrocarbon stapling strategy was exploited here for the structural modification of KR-12, the core and minimal fragment of LL-37.
Results: Based on a library of KR-12 derivatives that designed and synthesized to be stapled at positions of either i, i+4 or i, i+7, structure to activity relationship was investigated. Among them, KR-12(Q5, D9) with the glutamine and aspartic acid residues stapled displayed increased helical content and positive charge. The reinforced α-helical conformation not only protected it from proteolytic hydrolysis but also improved its antibacterial efficacy via effective membrane perturbation and anti-inflammatory efficacy via compact LPS binding. Besides, the increased positive charge endowed it with an enhanced therapeutic index. On infected wound mouse model, it was demonstrated to eliminate bacteria and promote wound closure and regeneration effectively.
Conclusion: Overall, the all-hydrocarbon stapling was proven to lay the foundation for the future development of antibacterial agents. KR-12(Q5, D9) could serve as a lead compound for the clinical treatment of bacterial infections.
Keywords: LL-37, all-hydrocarbon stapling, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, infected wound healing
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact