13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(5):2075-2098. doi:10.7150/thno.93919 This issue Cite
Review
Unleashing the potential of adipose organoids: A revolutionary approach to combat obesity-related metabolic diseases
1. Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
2. Shanghai Institute for Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Shanghai, China.
Abstract
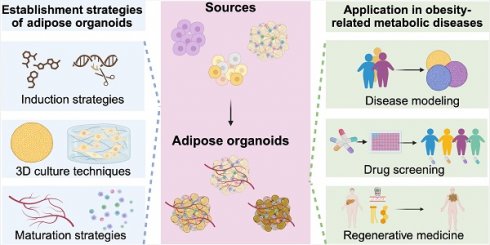
Obesity-related metabolic diseases, including obesity, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases pose a significant threat to health. However, comprehensive pathogenesis exploration and effective therapy development are impeded by the limited availability of human models. Notably, advances in organoid technology enable the generation of adipose organoids that recapitulate structures and functions of native human adipose tissues to investigate mechanisms and develop corresponding treatments for obesity-related metabolic diseases. Here, we review the general principles, sources, and three-dimensional techniques for engineering adipose organoids, along with strategies to promote maturation. We also outline the application of white adipose organoids, primarily for disease modeling and drug screening, and highlight the therapeutic potential of thermogenic beige and brown adipose organoids in promoting weight loss and glucose and lipid metabolic homeostasis. We also discuss the challenges and prospects in the establishment and bench-to-bedside of adipose organoids, as well as their potential applications.
Keywords: Adipose organoid, Obesity, Type 2 diabetes mellitus, Metabolic disease, Brown adipose tissue
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact