13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(5):2127-2150. doi:10.7150/thno.91626 This issue Cite
Research Paper
An advanced comprehensive muti-cell-type-specific model for predicting anti-PD-1 therapeutic effect in melanoma
1. Department of Musculoskeletal Oncology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center; Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, P. R. China.
2. Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University; Cancer center, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, P. R. China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
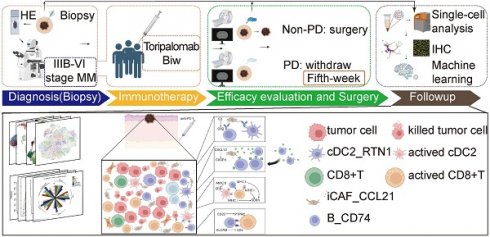
Rationale: Immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting the programmed cell death (PD)-1/PD-L1 pathway have promise in patients with advanced melanoma. However, drug resistance usually results in limited patient benefits. Recent single-cell RNA sequencing studies have elucidated that MM patients display distinctive transcriptional features of tumor cells, immune cells and interstitial cells, including loss of antigen presentation function of tumor cells, exhaustion of CD8+T and extracellular matrix secreted by fibroblasts to prevents immune infiltration, which leads to a poor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). However, cell subgroups beneficial to anti-tumor immunity and the model developed by them remain to be further identified.
Methods: In this clinical study of neoadjuvant therapy with anti-PD-1 in advanced melanoma, tumor tissues were collected before and after treatment for single-nucleus sequencing, and the results were verified using multicolor immunofluorescence staining and public datasets.
Results: This study describes four cell subgroups which are closely associated with the effectiveness of anti-PD-1 treatment. It also describes a cell-cell communication network, in which the interaction of the four cell subgroups contributes to anti-tumor immunity. Furthermore, we discuss a newly developed predictive model based on these four subgroups that holds significant potential for assessing the efficacy of anti-PD-1 treatment.
Conclusions: These findings elucidate the primary mechanism of anti-PD-1 resistance and offer guidance for clinical drug administration for melanoma.
Keywords: anti-PD-1, immune checkpoint inhibitors, machine learning, malignant melanoma, tumor microenvironment
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact