13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(8):2339-2349. doi:10.7150/thno.17555 This issue Cite
Research Paper
YD277 Suppresses Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Partially Through Activating the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway
1. Department of Laboratory Medicine & Central Laboratory, Southern Medical University Affiliated Fengxian Hospital, Shanghai, China, 201499;
2. Key Laboratory of Animal Models and Human Disease Mechanisms of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Yunnan Province, Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, China, 650223;
3. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Huizhou No.3 People's Hospital, Affiliated hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Huizhou, Guangdong, China, 516002;
4. Fengxian District Center Hospital Graduate Student Training Base, Jinzhou Medical University, Shanghai, China, 201499;
5. Chemical Biology Program, Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, Texas, 77555, United States.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
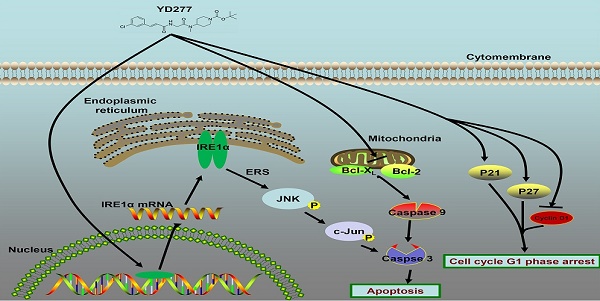
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive malignancy with poor clinical outcomes. YD277 is a novel small molecule derived from ML264, a KLF5 inhibitor that elicits cytotoxic effects in colon cancer cell lines. Our previous studies suggest that Krüpple-like factor 5 (KLF5) is a promising therapeutic target for TNBC. In this study, we demonstrated that YD277 significantly induced G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 TNBC cells, independent of KLF5 inhibition. YD277 also reduced the protein expression levels of Cyclin D1, Bcl2 and Bclxl and promoted the expression of p21 and p27. Moreover, the pro-apoptotic activity of YD277 in TNBC was mediated by the transcription of IRE1α, a key molecule in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathway. Finally, YD277 (15 mg/kg) significantly suppressed the growth of MDA-MB-231 tumor xenografts in nude mice. These findings indicate that YD277 is a promising chemotherapeutic candidate for TNBC.
Keywords: YD277, KLF5, Triple-Negative Breast Cancer, IRE1α, ER stress.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact