13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(7):2003-2016. doi:10.7150/thno.28057 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tolerizing CTL by Sustained Hepatic PD-L1 Expression Provides a New Therapy Approach in Mouse Sepsis
1. Institute of Biochemistry I, Faculty of Medicine, Goethe-University Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany.
2. Fraunhofer Institute for Molecular Biology and Applied Ecology IME, Project Group Translational Medicine & Pharmacology TMP, Frankfurt, Germany.
3. Pharmazentrum/ZAFES Frankfurt, Faculty of Medicine, Goethe-University Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany.
4. Institute for Vascular Signalling, Centre for Molecular Medicine, Goethe-University Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany.
5. Institute for Cardiovascular Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Goethe-University Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany.
6. Institute for Experimental Surgery, Rostock University Medical Center, Rostock, Germany.
7. Institute of Experimental Gene Therapy and Cancer Research, Rostock University Medical Center, Rostock, Germany.
8. King's College London, British Heart Foundation, Centre of Excellence, The James Black Centre, London, UK.
9. Georg Speyer Haus, Institute for Tumor Biology and Experimental Therapy, Frankfurt, Germany.
10. Institute for Medical Microbiology and Infection Control, University Hospital Frankfurt, Paul-Ehrlich-Str. 40, Frankfurt am Main, Germany.
Abstract
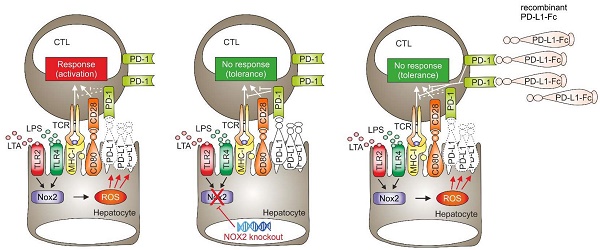
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) activation contributes to liver damage during sepsis, but the mechanisms involved are largely unknown. Understanding the underlying principle will permit interference with CTL activation and thus, provide a new therapeutic option.
Methods: To elucidate the mechanism leading to CTL activation we used the Hepa1-6 cell line in vitro and the mouse model of in vivo polymicrobial sepsis, following cecal-ligation and -puncture (CLP) in wildtype, myeloid specific NOX-2, global NOX2 and NOX4 knockout mice, and their survival as a final readout. In this in vivo setting, we also determined hepatic mRNA and protein expression as well as clinical parameters of liver damage - aspartate- and alanine amino-transaminases. Hepatocyte specific overexpression of PD-L1 was achieved in vivo by adenoviral infection and transposon-based gene transfer using hydrodynamic injection.
Results: We observed downregulation of PD-L1 on hepatocytes in the murine sepsis model. Adenoviral and transposon-based gene transfer to restore PD-L1 expression, significantly improved survival and reduced the release of liver damage, as PD-L1 is a co-receptor that negatively regulates T cell function. Similar protection was observed during pharmacological intervention using recombinant PD-L1-Fc. N-acetylcysteine blocked the downregulation of PD-L1 suggesting the involvement of reactive oxygen species. This was confirmed in vivo, as we observed significant upregulation of PD-L1 expression in NOX4 knockout mice, following sham operation, whereas its expression in global as well as myeloid lineage NOX2 knockout mice was comparable to that in the wild type animals. PD-L1 expression remained high following CLP only in total NOX2 knockouts, resulting in significantly reduced release of liver damage markers.
Conclusion: These results suggest that, contrary to common assumption, maintaining PD-L1 expression on hepatocytes improves liver damage and survival of mice during sepsis. We conclude that administering recombinant PD-L1 or inhibiting NOX2 activity might offer a new therapeutic option in sepsis.
Keywords: sepsis, cytotoxic T cells, reactive oxygen species, PD-L1, liver
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact