13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(15):4375-4390. doi:10.7150/thno.33688 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Autophagy impairment contributes to PBDE-47-induced developmental neurotoxicity and its relationship with apoptosis
1. Department of Occupational and Environmental Health, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, People's Republic of China
2. Key Laboratory of Environment and Health, Ministry of Education & Ministry of Environmental Protection, State Key Laboratory of Environmental health (incubating), School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, People's Republic of China
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
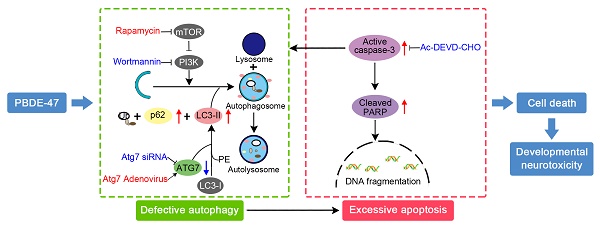
Apoptosis is involved in 2,2',4,4'- tetrabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-47)-induced developmental neurotoxicity. However, little is known about the role of autophagy, especially its relationship with apoptosis underlying such neurotoxic process.
Methods: Using female Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to low-dose PBDE-47 (0.1, 1.0 and 10 mg/kg/day) from pre-pregnancy until weaning of offspring to mimic human exposure, we investigated the effects of PBDE-47 on autophagy and apoptosis in relation to cognitive impairment of adult offspring rats. We also evaluated relationship between autophagy and apoptosis using neuroendocrine pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells, a widely used neuron-like cell line for neuronal development.
Results: In vivo, perinatal exposure to PBDE-47 induced memory deficits in adult rats. This is accompanied by hippocampal neuronal loss partly as a result of apoptosis, as evidenced by caspase-3 activation and PARP cleavage. Further study identified that PBDE-47 triggered autophagic vesicles accumulation, increased levels of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3)-II, an essential protein for autophagosomes formation, and autophagy substrate sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1/p62), but reduced levels of autophagy-related protein (ATG) 7, a key protein for autophagosomes elongation, suggestive of autophagy impairment. These findings were further demonstrated by an in vitro model of PBDE-47-treated PC12 cells. Mechanistically, autophagy alteration is more sensitive to PBDE-47 treatment than apoptosis induction. Importantly, while stimulation of autophagy by the chemical inducer rapamycin and adenovirus-mediated Atg7 overexpression aggravated PBDE-47-induced apoptosis and cell death, inhibition of autophagy by the chemical inhibitor wortmannin and siRNA knockdown of Atg7 reversed PBDE-47-produced detrimental outcomes. Interestingly, blockage of apoptosis by caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO ameliorated PBDE-47-exerted autophagy impairment and cell death, though in combination with autophagy inhibitor did not further promote cell survival.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that autophagy impairment facilitates apoptosis, which, in turn, disrupts autophagy, ultimately resulting in cell death, and that autophagy may act as a promising therapeutic target for PBDE-47-induced developmental neurotoxicity.
Keywords: PBDE-47, developmental neurotoxicity, apoptosis, autophagy, relationship
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact