13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(24):7239-7250. doi:10.7150/thno.35573 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Genome-wide discovery and validation of diagnostic DNA methylation-based biomarkers for hepatocellular cancer detection in circulating cell free DNA
1. Department of Molecular Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
2. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, College of Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
3. Department of Health Sciences Research, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, USA
4. Department of Transplantation, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, USA
5. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, New Jersey Medical School, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, Newark, NJ, USA
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer, is growing in incidence but treatment options remain limited, particularly for late stage disease. As liver cirrhosis is the principal risk state for HCC development, markers to detect early HCC within this patient population are urgently needed. Perturbation of epigenetic marks, such as DNA methylation (5mC), is a hallmark of human cancers, including HCC. Identification of regions with consistently altered 5mC levels in circulating cell free DNA (cfDNA) during progression from cirrhosis to HCC could therefore serve as markers for development of minimally-invasive screens of early HCC diagnosis and surveillance.
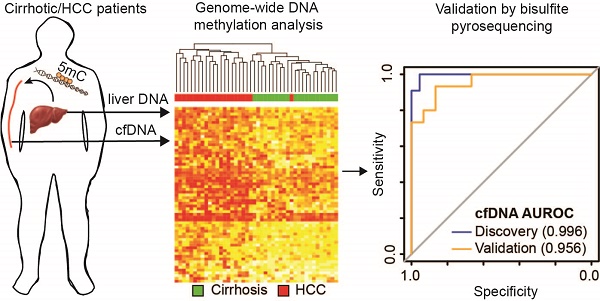
Methods: To discover DNA methylation derived biomarkers of HCC in the background of liver cirrhosis, we profiled genome-wide 5mC landscapes in patient cfDNA using the Infinium HumanMethylation450k BeadChip Array. We further linked these findings to primary tissue data available from TCGA and other public sources. Using biological and statistical frameworks, we selected CpGs that robustly differentiated cirrhosis from HCC in primary tissue and cfDNA followed by validation in an additional independent cohort.
Results: We identified CpGs that segregate patients with cirrhosis, from patients with HCC within a cirrhotic liver background, through genome-wide analysis of cfDNA 5mC landscapes. Lasso regression analysis pinpointed a panel of probes in our discovery cohort that were validated in two independent datasets. A panel of five CpGs (cg04645914, cg06215569, cg23663760, cg13781744, and cg07610777) yielded area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curves of 0.9525, 0.9714, and 0.9528 in cfDNA discovery and tissue validation cohorts 1 and 2, respectively. Validation of a 5-marker panel created from combining hypermethylated and hypomethylated CpGs in an independent cfDNA set by bisulfite pyrosequencing yielded an AUROC of 0.956, compared to the discovery AUROC of 0.996.
Conclusion: Our finding that 5mC markers derived from primary tissue did not perform well in cfDNA, compared to those identified directly from cfDNA, reveals potential advantages of starting with cfDNA to discover high performing markers for liquid biopsy development.
Keywords: liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular cancer, biomarker, epigenetics, cfDNA, DNA methylation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact