13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(2):671-686. doi:10.7150/thno.39863 This issue Cite
Review
Carbon Dots as Potent Antimicrobial Agents
1. Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Biomanufacturing Research Institute and Technology Enterprise, North Carolina Central University, Durham, NC 27707, USA
2. Department of Chemistry and Laboratory for Emerging Materials and Technology, Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina 29634, USA
3. Department of Natural Sciences, Northwest Missouri State University, Maryville, Missouri 64468, USA
Abstract
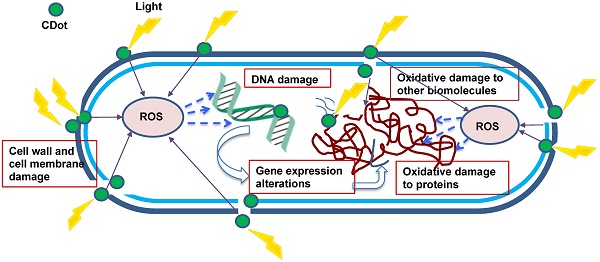
Carbon dots (CDots) have emerged to represent a highly promising new platform for visible/natural light-activated microbicidal agents. In this article, the syntheses, structures, and properties of CDots are highlighted, representative studies on their activities against bacteria, fungi, and viruses reviewed, and the related mechanistic insights discussed. Also highlighted and discussed are the excellent opportunities for potentially extremely broad applications of this new platform, including theranostics uses.
Keywords: carbon dots, antimicrobial, light activation, photodynamic effect, reactive oxygen species, multi-drug resistance.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact