13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(22):10200-10212. doi:10.7150/thno.48706 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Radiologist-like artificial intelligence for grade group prediction of radical prostatectomy for reducing upgrading and downgrading from biopsy
1. School of Computer Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, China.
2. CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Beijing Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, the State Key Laboratory of Management and Control for Complex Systems, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
3. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China.
4. Urology and lithotripsy center, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing, China.
5. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China.
6. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China.
7. LIST, Key Laboratory of Computer Network and Information Integration, Southeast University, Ministry of Education, Nanjing, China.
8. Engineering Research Center of Molecular and Neuro Imaging of Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, Xidian University, Xi'an, China.
9. CAS Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
10. Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Big Data-Based Precision Medicine, School of Medicine and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, China.
11. Key Laboratory of Big Data-Based Precision Medicine (Beihang University),Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Beijing, China.
12. School of Artificial Intelligence, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100080, China.
#Co-first authors with equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
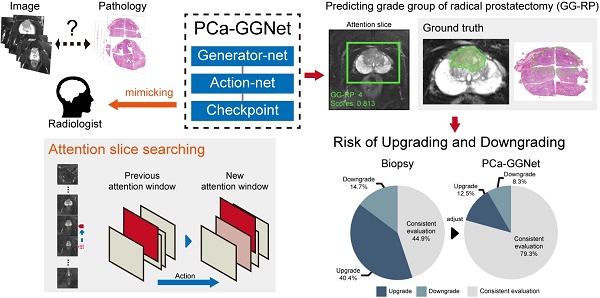
Rationale: To reduce upgrading and downgrading between needle biopsy (NB) and radical prostatectomy (RP) by predicting patient-level Gleason grade groups (GGs) of RP to avoid over- and under-treatment.
Methods: In this study, we retrospectively enrolled 575 patients from two medical institutions. All patients received prebiopsy magnetic resonance (MR) examinations, and pathological evaluations of NB and RP were available. A total of 12,708 slices of original male pelvic MR images (T2-weighted sequences with fat suppression, T2WI-FS) containing 5405 slices of prostate tissue, and 2,753 tumor annotations (only T2WI-FS were annotated using RP pathological sections as ground truth) were analyzed for the prediction of patient-level RP GGs. We present a prostate cancer (PCa) framework, PCa-GGNet, that mimics radiologist behavior based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL). We developed and validated it using a multi-center format.
Results: Accuracy (ACC) of our model outweighed NB results (0.815 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.773-0.857] vs. 0.437 [95% CI: 0.335-0.539]). The PCa-GGNet scored higher (kappa value: 0.761) than NB (kappa value: 0.289). Our model significantly reduced the upgrading rate by 27.9% (P < 0.001) and downgrading rate by 6.4% (P = 0.029).
Conclusions: DRL using MRI can be applied to the prediction of patient-level RP GGs to reduce upgrading and downgrading from biopsy, potentially improving the clinical benefits of prostate cancer oncologic controls.
Keywords: prostate cancer, Gleason grade groups, deep reinforcement learning, prostate cancer grading, magnetic resonance imaging
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact