13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(16):7422-7435. doi:10.7150/thno.42167 This issue Cite
Review
Current understanding of the role of Adipose-derived Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolic Homeostasis and Diseases: Communication from the distance between cells/tissues
1. Department of Endocrinology, Health Management Center, Tianjin Union Medical Center, Nankai University Affiliated Hospital, Tianjin, 300121, P.R. China.
2. Department of Dermatology, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania.
3. Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
4. Shanghai National Research Centre for Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, State Key Laboratory of Medical Genomics, Shanghai Institute for Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this review.
Abstract
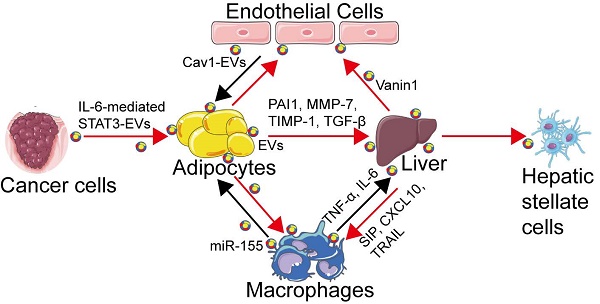
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) including exosomes, microvesicles (MVs), and apoptotic bodies, are small membrane vesicular structures that are released during cell activation, senescence, or programmed cell death, including apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis. EVs serve as novel mediators for long-distance cell-to-cell communications and can transfer various bioactive molecules, such as encapsulated cytokines and genetic information from their parental cells to distant target cells. In the context of obesity, adipocyte-derived EVs are implicated in metabolic homeostasis serving as novel adipokines. In particular, EVs released from brown adipose tissue or adipose-derived stem cells may help control the remolding of white adipose tissue towards browning and maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Interestingly, EVs may even serve as mediators for the transmission of metabolic dysfunction across generations. Also, EVs have been recognized as novel modulators in various metabolic disorders, including insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. In this review, we summarize the latest progress from basic and translational studies regarding the novel effects of EVs on metabolic diseases. We also discuss EV-mediated cross-talk between adipose tissue and other organs/tissues that are relevant to obesity and metabolic diseases, as well as the relevant mechanisms, providing insight into the development of new therapeutic strategies in obesity and metabolic diseases.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles, inflammation, adipose tissue, obesity, metabolic disease
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact