13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(19):8721-8743. doi:10.7150/thno.41648 This issue Cite
Review
Stem cell programs in cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance
1. The Ken & Ruth Davee Department of Neurology, Lou and Jean Malnati Brain Tumor Institute, The Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL 60611, USA
2. Department of Pathology, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL 60611, USA
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
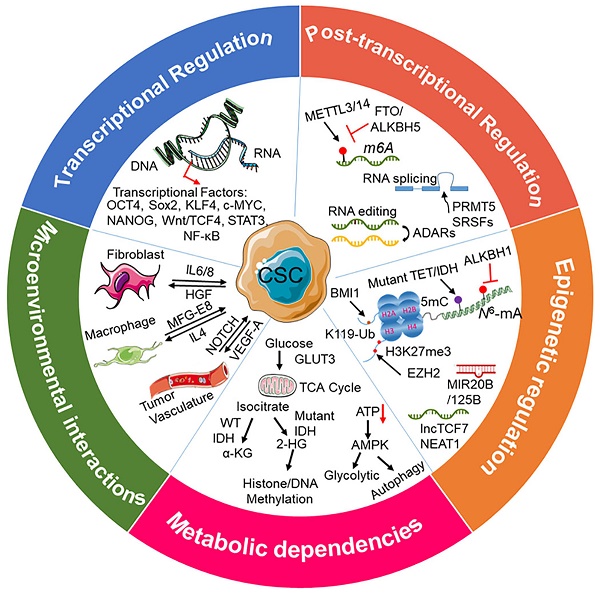
Over the past few decades, substantial evidence has convincingly revealed the existence of cancer stem cells (CSCs) as a minor subpopulation in cancers, contributing to an aberrantly high degree of cellular heterogeneity within the tumor. CSCs are functionally defined by their abilities of self-renewal and differentiation, often in response to cues from their microenvironment. Biological phenotypes of CSCs are regulated by the integrated transcriptional, post-transcriptional, metabolic, and epigenetic regulatory networks. CSCs contribute to tumor progression, therapeutic resistance, and disease recurrence through their sustained proliferation, invasion into normal tissue, promotion of angiogenesis, evasion of the immune system, and resistance to conventional anticancer therapies. Therefore, elucidation of the molecular mechanisms that drive cancer stem cell maintenance, plasticity, and therapeutic resistance will enhance our ability to improve the effectiveness of targeted therapies for CSCs. In this review, we highlight the key features and mechanisms that regulate CSC function in tumor initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. We discuss factors for CSC therapeutic resistance, such as quiescence, induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and resistance to DNA damage-induced cell death. We evaluate therapeutic approaches for eliminating therapy-resistant CSC subpopulations, including anticancer drugs that target key CSC signaling pathways and cell surface markers, viral therapies, the awakening of quiescent CSCs, and immunotherapy. We also assess the impact of new technologies, such as single-cell sequencing and CRISPR-Cas9 screening, on the investigation of the biological properties of CSCs. Moreover, challenges remain to be addressed in the coming years, including experimental approaches for investigating CSCs and obstacles in therapeutic targeting of CSCs.
Keywords: cancer stem cells, transcriptional and posttranslational regulation, epigenetics, metabolism, tumor microenvironment, therapy resistance, CSC-targeting therapies
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact