13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(22):9913-9922. doi:10.7150/thno.46417 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of Pendrin by a small molecule reduces Lipopolysaccharide-induced acute Lung Injury
1. Division of Pulmonology, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea.
2. Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Chest Diseases, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
3. Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
4. The Airway Mucus Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
5. College of Pharmacy, Yonsei Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Yonsei University, Incheon, South Korea.
6. Department of Integrated OMICS for Biomedical Science, Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea.
7. Translational Research Center for Protein Function Control, Department of Biotechnology, Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea.
8. Department of Anatomy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
9. Severance Biomedical Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine.
10. Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine.
11. Laboratory of Developmental Biology and Genomics, BK21 Plus Program for Advanced Veterinary Science and Research Institute for Veterinary Science, College of Veterinary Medicine, and Korea Mouse Phenotyping Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea.
12. Interdisciplinary Program for Bioinformatics, Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea.
13. Research Institute, National Cancer Center, South Korea.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
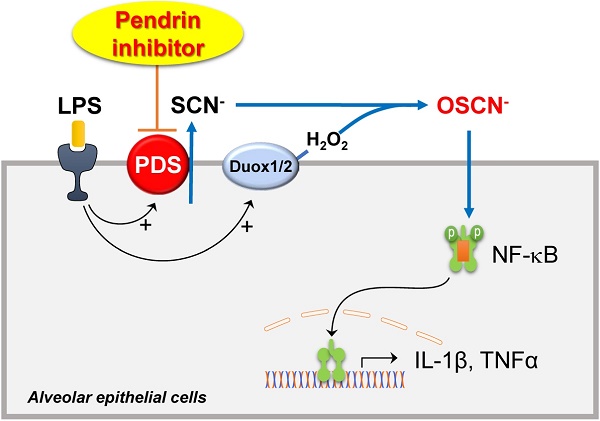
Rationale: Pendrin is encoded by SLC26A4 and its mutation leads to congenital hearing loss. Additionally, pendrin is up-regulated in inflammatory airway diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, allergic rhinitis, and asthma. In this study, the effects of a novel pendrin inhibitor, YS-01, were investigated in an LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI) mice model, and the mechanism underlying the effect of YS-01 was examined.
Methods: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 mg/kg) was intranasally instilled in wild type (WT) and pendrin-null mice. YS-01 (10 mg/kg) was administered intra-peritoneally before or after LPS inhalation. Lung injury parameters were assessed in the lung tissue and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Pendrin levels in the BALF of 41 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) due to pneumonia and 25 control (solitary pulmonary nodule) patients were also measured.
Results: LPS instillation induced lung injury in WT mice but not in pendrin-null mice. Pendrin expression was increased by LPS stimulation both in vitro and in vivo. YS-01 treatment dramatically attenuated lung injury and reduced BALF cell counts and protein concentration after LPS instillation in WT mice. Proinflammatory cytokines and NF-κB activation were suppressed by YS-01 treatment in LPS-induced ALI mice. In BALF of patients whose ARDS was caused by pneumonia, pendrin expression was up-regulated compared to that in controls (mean, 24.86 vs. 6.83 ng/mL, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: A novel pendrin inhibitor, YS-01, suppressed lung injury in LPS-induced ALI mice and our data provide a new strategy for the treatment of inflammatory airway diseases including sepsis-induced ALI.
Keywords: pendrin, inhibitor, SLC26A4, ALI, ARDS
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact