13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(11):4879-4903. doi:10.7150/thno.72812 This issue Cite
Review
Extracellular vesicles as bioactive nanotherapeutics: An emerging paradigm for regenerative medicine
1. Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine and Biotherapy, School of Life Sciences, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, P. R. China.
2. International Medical Center, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100050, P. R. China.
3. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Jinan University First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou, 510630, P. R. China.
Abstract
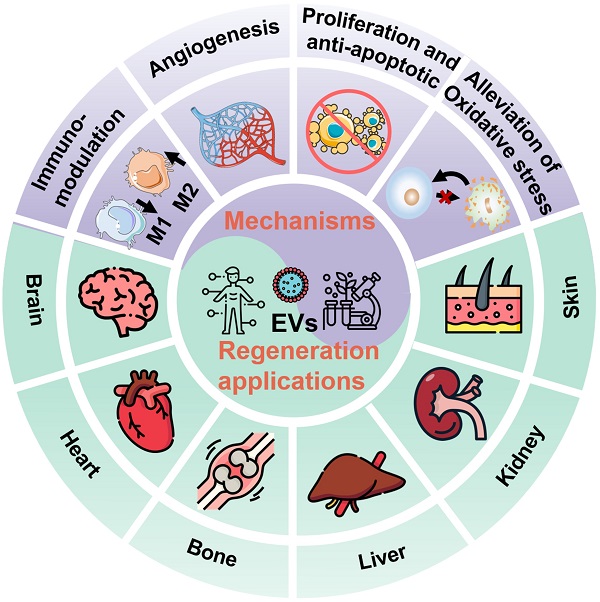
In recent decades, extracellular vesicles (EVs), as bioactive cell-secreted nanoparticles which are involved in various physiological and pathological processes including cell proliferation, immune regulation, angiogenesis and tissue repair, have emerged as one of the most attractive nanotherapeutics for regenerative medicine. Herein we provide a systematic review of the latest progress of EVs for regenerative applications. Firstly, we will briefly introduce the biogenesis, function and isolation technology of EVs. Then, the underlying therapeutic mechanisms of the native unmodified EVs and engineering strategies of the modified EVs as regenerative entities will be discussed. Subsequently, the main focus will be placed on the tissue repair and regeneration applications of EVs on various organs including brain, heart, bone and cartilage, liver and kidney, as well as skin. More importantly, current clinical trials of EVs for regenerative medicine will also be briefly highlighted. Finally, the future challenges and insightful perspectives of the currently developed EV-based nanotherapeutics in biomedicine will be discussed. In short, the bioactive EV-based nanotherapeutics have opened new horizons for biologists, chemists, nanoscientists, pharmacists, as well as clinicians, making possible powerful tools and therapies for regenerative medicine.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles, exosomes, nanotherapeutics, tissue regeneration, regenerative mechanisms, EV engineering strategy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact