13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(13):4601-4614. doi:10.7150/thno.86547 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The spatial coexistence of TIGIT/CD155 defines poorer survival and resistance to adjuvant chemotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Department of Pathology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College and Chinese Academy of Medical Science, Beijing, 100730, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
#These authors jointly supervised this work.
Abstract
Background: Targeting emerging T cell immunoreceptor with immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT)/CD155 axis shows promise for restoring anti-tumor immunity, but its immune phenotypes and prognostic significance in a large cohort of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) are limited.
Methods: Three seven-color multispectral panels were rationally designed to investigate the protein expression, immune-microenvironmental feature, prognostic value, and the response to adjuvant chemotherapy of TIGIT/CD155 in 272 PDAC specimens using multiplex immunohistochemistry.
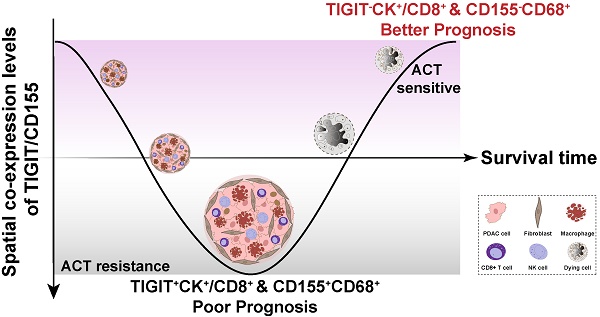
Results: We revealed low immunogenicity and high heterogeneity of the PDAC immune microenvironment featured by abundant CD3+ T cells and CD68+ macrophages and low infiltration of activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes. TIGIT and CD155 were highly expressed in PDAC tissues compared to paracancerous tissues. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes expressing TIGIT were correlated with high densities of CD45RO+ T cells; TIGTI+CD8+ T cells were associated with high infiltration of CD3+CD45RO+FOXP3+. CD155+CK+ were significantly related to high densities of CD3+ and CD3+CD8+CD45RO+ T cells. High positive rates for TIGIT in TCs, CD8+ T cells, and CD155 in macrophages were correlated with poor progression-free and disease-specific survival, respectively, and their clinical significance was correlated with PD-L1 status. Notably, spatial co-existence of TIGIT+CK+ or TIGIT+CD8+ and CD155+CD68+ indicated poor survival and resistance to adjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with PDAC.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that targeting TIGIT/CD155 immunosuppressive axis may guide patient stratification and improve the clinical outcome of PDAC.
Keywords: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, TIGIT/CD155, PD-L1, adjuvant chemotherapy, multiplex immunohistochemistry
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact